Trends in antidote use in France from 2015 to 2021: a nationwide poison centers study
- PMID: 40826216
- PMCID: PMC12361460
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-15475-x
Trends in antidote use in France from 2015 to 2021: a nationwide poison centers study
Abstract
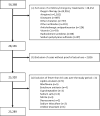
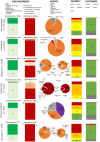
The French Poison Centers database is a tool of choice for the analysis of poisoning cases requiring the administration of an antidote although not all uses are systematically reported. This national retrospective study aims to report trends of use of antidotes in France over a 7-year period from 2015 to 2021. A total of 25,289 cases of poisoning required the administration of an antidote, among which 46.7% were moderate to severe. While 77.1% of poisonings progressed toward recovery, the observed mortality rate was 1.7%. The 3 most frequently used antidotes according to data from Poison Centers were N-acetylcysteine (n = 13,555 [53.6%]), flumazenil (n = 3102 [12.3%]) and naloxone (n = 1740 [6.9%]) reflecting the most common types of poisoning involving acetaminophen, benzodiazepines, and opioids. The observed use of methylthioninium chloride, hydroxocobalamin, cyanocobalamin and DOAC reversal agents increased, both in terms of absolute numbers and proportions, revealing new behaviors leading to poisoning, such as nitrous oxide consumption. Conversely, the observed use of ethanol-based therapy, L-carnitine, and dantrolene decreased over time, reflecting both current medical practices and shifts in guidelines. This study provides a novel insight into the typology (circumstances, severity, development) of poisonings requiring an antidote, as well as the description of the causative agents.
Keywords: Antidotes; Poison center; Poisonings.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Prevention and management of cases of poisoning. https://www.who.int/teams/environment-climate-change-and-health/chemical... (2024).
-
- Deaths from poisoning, part of the following publication: Esteban Ortiz-Ospina and Max Roser (2016) - “Global Health”. Data adapted from IHME, Global Burden of Disease. https://archive.ourworldindata.org. Our World in Data. https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/deaths-from-poisoning (2025).
-
- Karami M. Principles of toxicotherapy: General & special therapy.
-
- Al-Sohaim, S. I., Awang, R., Zyoud, S. H., Rashid, S. M. D. & Hashim, S. Evaluate the impact of hospital types on the availability of antidotes for the management of acute toxic exposures and poisonings in Malaysia. Hum. Exp. Toxicol.31(3), 274–281 (2012). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

