Genome-wide identification of VOZ gene family in ten cotton species and the function analysis of GhVOZ2 involved in heat stress response
- PMID: 40826317
- PMCID: PMC12362909
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-025-11957-4
Genome-wide identification of VOZ gene family in ten cotton species and the function analysis of GhVOZ2 involved in heat stress response
Abstract
Background: Vascular plant one zinc-finger protein (VOZ) is a type of special transcription factor and plays important roles in regulating various biological processes in plants. However, a genome-wide analysis of VOZ gene family in cotton is still not clear, which greatly limits the further understanding of VOZ gene function and regulatory mechanism.
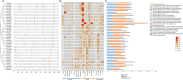
Results: We identified 44 VOZ family genes in ten cotton species including 3 in Gossypium herbaceum, G. arboretum, G. thurberi, and G. Raimondii, 6 in G. hirsutum, G. barbadense, G. tomentosum, and G. mustelinum, and 5 in G. darwinii. The phylogenetic tree analysis indicated that VOZ gene family was subdivided into four subgroups. Chromosome location and collinearity analysis revealed that this gene family had experienced segment duplication events. The exon-intron structure and conserved motif analysis showed high conservations in each branch of the cotton VOZ genes. Cis-acting element component analysis displayed that VOZ gene family may be involved in various stresses. Expression profile analysis of GhVOZ genes through both publicly available RNA-seq data from G. hirsutum and quantitative reverse transcription PCR (RT-qPCR) indicated that GhVOZ members are involved in tissue development and biotic and abiotic responses, especially GhVOZ2 showed continuous high expressions in different tissues and stress treatments, with the most significantly induced accumulation under heat stress. Suppressing GhVOZ2 expression in virus-induced silencing (VIGS) cotton lines significantly decreased the tolerance to heat stress. Further RNA-seq analysis of TRV::GhVOZ2 showed that the down-regulated differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were mainly enriched in hormone signal pathways (auxin and BRs), phenylpropanoid and flavonoid biosynthesis, fatty acid elongation, starch and sucrose metabolism pathways, suggesting their potential important roles in heat response mediated by GhVOZ2.
Conclusions: A total of 44 VOZ genes were obtained in ten cotton species, and GhVOZ2 might perform significant positive function in cotton in response to heat stress via regulating the pathways of hormone signal and metabolisms. Our results provide insights into the function and regulatory mechanism of VOZ gene family and the further utilization of excellent cotton material breeding.
Keywords: VOZ gene family; Cotton; Heat stress; RNA-seq; Virus-induced gene silencing.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of DUF789 genes in cotton: implications for fibre development.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Sep 2;25(1):1192. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-07258-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40898020 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Genome-wide identification analysis of aldo-keto reductase gene family in cotton and GhAKR40 role in salt stress tolerance.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Sep 8;25(1):187. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01678-y. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40920257
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Mitsuda N, Hisabori T, Takeyasu K et al. VOZ; isolation and characterization of novel vascular plant transcription factors with a one-zinc finger from Arabidopsis Thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004;45(7)845– 54. - PubMed
-
- Jensen Michael K, Kjaersgaard T, Nielsen Michael M, et al. The Arabidopsis Thaliana NAC transcription factor family: structure–function relationships and determinants of ANAC019 stress signalling [J]. Biochem J. 2010;426(2):183–96. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- CXBJ202309/Science and Technology Project of Shihezi University
- 2023ZD052/Science and Technology Project of Bingtuan
- 2022TSYCCX0121/Tianshan Talent Project of Xinjiang
- XL202403/The projects sponsored by the development fund for Xinjiang talents XL
- 2024A02002-3/Science and Technology Project of Xinjiang
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

