Retrospective study on the value of serum angiopoietin 2 and cystatin C levels in the early diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome
- PMID: 40826711
- PMCID: PMC12367013
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043650
Retrospective study on the value of serum angiopoietin 2 and cystatin C levels in the early diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome
Abstract
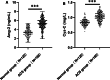
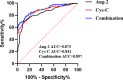
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is a coronary emergency that arises from myocardial ischemia and thrombosis and can be triggered by the rupture of a subcutaneous unstable plaque within the coronary artery or coronary artery erosion. The current study aimed to calculate the predictive value of serum angiopoietin 2 (Ang-2) and cystatin C (Cys-C) levels in the early diagnosis of ACS. We retrospectively analyzed data from 180 patients diagnosed with ACS at our hospital between January 2023 and June 2024, with 120 healthy volunteers serving as the control group during the same period. Clinical baseline and pathological data were recorded for all participants, and serum levels of Ang-2 and Cys-C were determined using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit. The correlation between serum Ang-2, Cys-C levels, and Gensini scores in patients with ACS was analyzed using Spearman or Pearson correlation coefficients, respectively. Independent risk factors for ACS were analyzed using multivariate logistic regression. A receiver operating characteristic curve was used to analyze the predictive value of serum Ang-2, Cys-C, or Ang-2 combined with Cys-C for the early diagnosis of ACS. Serum Ang-2 and Cys-C levels in patients with ACS were significantly higher than those in the normal group. Serum Ang-2 and Cys-C levels significantly and positively correlated with Gensini scores in patients with ACS. Logistic multivariate regression analysis revealed that total cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, Ang-2, and Cys-C were independent risk factors for ACS. The area under the curve of serum Ang-2 combined with Cys-C was 0.897 (sensitivity, 77.22%; specificity, 87.50%) in patients with ACS, and its diagnostic efficacy was higher than that of Ang-2 or Cys-C alone. Serum Ang-2 and Cys-C are highly expressed in patients with ACS, and serum Ang-2 combined with Cys-C has a high predictive value for the early diagnosis of ACS.
Keywords: Ang-2; Cys-C; ROC; acute coronary syndrome; early diagnosis; independent risk factor.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Barstow C. Acute coronary syndrome: presentation and diagnostic evaluation. FP Essent. 2020;490:11–9. - PubMed
-
- Shi Z, Zhao C, Hu J, et al. The application of traditional Chinese medicine injection on patients with acute coronary syndrome during the perioperative period of percutaneous coronary intervention: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:3834128. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

