PD-L1/ITGB4 Axis Modulates Sensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Sorafenib via FAK/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 40827229
- PMCID: PMC12358154
- DOI: 10.2147/ITT.S534782
PD-L1/ITGB4 Axis Modulates Sensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Sorafenib via FAK/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway
Abstract
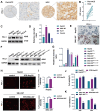
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) frequently develops resistance to sorafenib, a first-line treatment for advanced HCC. While PD-L1 contributes to immune evasion and direct tumor survival, its role in modulating sorafenib resistance via non-immunological pathways remains unclear. This study investigates the PD-L1/ITGB4 axis in regulating sorafenib sensitivity.
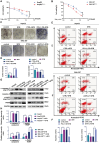
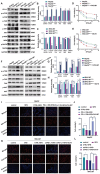
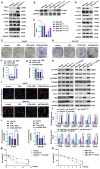
Methods: Bioinformatics analysis of HCC datasets identified PD-L1/ITGB4 co-expression. Protein interaction was validated via co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP). Functional impacts on FAK/AKT/mTOR signaling were assessed using kinase inhibitors and gene knockdown in HCC cell lines. Sorafenib sensitivity was evaluated in vitro and in xenograft models with mono- and combination therapies (PD-L1/ITGB4 inhibition ± sorafenib).
Results: PD-L1 directly interacts with ITGB4 to activate the FAK/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, independent of its immune-regulatory functions. This interaction critically mediates sorafenib resistance in HCC, as evidenced by significantly reduced drug sensitivity in PD-L1high/ITGB4high cells (p < 0.001). Crucially, genetic knockdown of either PD-L1 or ITGB4 effectively reversed this chemoresistance phenotype. In translational validation, combined pharmacological inhibition of the PD-L1/ITGB4 axis with sorafenib synergistically suppressed tumor progression in vivo, achieving >60% greater volume reduction compared to monotherapies.
Conclusion: The PD-L1/ITGB4 axis drives sorafenib resistance via FAK/AKT/mTOR hyperactivation. Dual targeting of PD-L1/ITGB4 enhances sorafenib efficacy, revealing a tumor-intrinsic mechanism and proposing a novel combinatorial strategy for HCC.
Keywords: FAK/AKT/mTOR; hepatocellular carcinoma; integrin beta 4; programmed cell death ligand-1; resistance.
© 2025 Zhu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Matrix stiffness-dependent PD-L2 deficiency improves SMYD3/xCT-mediated ferroptosis and the efficacy of anti-PD-1 in HCC.J Adv Res. 2025 Jul;73:265-282. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.08.021. Epub 2024 Aug 17. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 39159723 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting USP47 enhances immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma by destabilizing PD-L1.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Aug 28;161:115024. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.115024. Epub 2025 Jun 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40494207
-
Downregulation of PD-L1 expression by Wnt pathway inhibition to enhance PD-1 blockade efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma.Biol Direct. 2025 Apr 10;20(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13062-025-00645-8. Biol Direct. 2025. PMID: 40211365 Free PMC article.
-
Benefits of combination therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors and predictive role of tumour mutation burden in hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Nov;112:109244. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109244. Epub 2022 Sep 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36126410
-
Comparison of efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 combination therapy in first-line treatment of advanced NSCLC: an updated systematic review and network meta-analysis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2024 Oct;26(10):2488-2502. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03442-3. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38625495
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

