Role of Interleukin-6 in Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: Focus on the JAK/STAT Pathway and Macrophage Polarization
- PMID: 40827265
- PMCID: PMC12358124
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S530754
Role of Interleukin-6 in Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: Focus on the JAK/STAT Pathway and Macrophage Polarization
Abstract
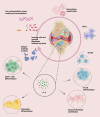
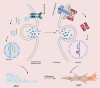
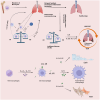
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disorder characterized by chronic synovitis and extra-articular manifestations (EAMs), with interstitial lung disease (ILD) being a leading cause of mortality. Interleukin-6 (IL-6), a pivotal cytokine in RA pathogenesis, drives both articular and pulmonary inflammation through its involvement in immune dysregulation and fibrotic processes. This review elucidates the molecular mechanisms by which IL-6 contributes to rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD) progression, particularly via the Janus kinases (JAK)/signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) signaling pathway and macrophage polarization. Additionally, we objectively evaluate current and emerging therapeutic strategies targeting IL-6 and downstream pathways.
Keywords: IL-6; JAK/STAT signaling; RA-ILD; macrophage polarization; targeted therapy.
© 2025 Yu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors of this manuscript report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
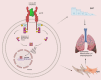
Similar articles
-
DS-Modified Paeoniflorin pH-Responsive Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles for Targeted Macrophage Polarization in a Rat Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jul 12;20:8967-8992. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S516434. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40671689 Free PMC article.
-
Ruxolitinib attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice by modulating macrophage polarization through the JAK/STAT signaling pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Aug 28;161:114962. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114962. Epub 2025 Jun 3. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40466612
-
The immunomodulatory of interleukin-33 in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review.Clin Immunol. 2024 Aug;265:110264. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2024.110264. Epub 2024 May 31. Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38825072
-
Anti-Inflammatory Versus Antifibrotic Therapies for the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: Protocol for a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.JMIR Res Protoc. 2025 Jul 21;14:e73219. doi: 10.2196/73219. JMIR Res Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40690765 Free PMC article.
-
MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis: mechanisms and therapeutic potential.PeerJ. 2025 Jul 14;13:e19708. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19708. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40677749 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

