HIF-1 attenuates high-fiber diet-mediated proliferation and stemness of colonic epithelium
- PMID: 40827535
- PMCID: PMC12369635
- DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2025.2543123
HIF-1 attenuates high-fiber diet-mediated proliferation and stemness of colonic epithelium
Abstract
The complex interplay between diet, microbiota, and host is exemplified by the effects of dietary fiber on the intestine. Inulin ingestion triggers epithelial changes in the colon that depend on microbiota-derived molecules, including enhanced proliferation, increased mucus production, and elevated antimicrobial peptide secretion. Here we employed a multilayered and multi-omics approach, including dietary interventions, intestinal organoids, and both genetic and pharmacological interventions to investigate the impact of inulin on two aspects of diet-microbiota-host interactions: intestinal hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 signaling in intestinal epithelial cells (IECs). We found that inulin, a soluble fiber, promotes intestinal hypoxia, stabilizing HIF-1 in IECs in a microbiota- and host-dependent manner. Furthermore, we show that HIF-1 stabilization modulates intestinal stem cell (ISC) function through metabolic reprogramming in a microbiota-dependent manner. Our findings reveal an unrecognized role for HIF-1 in orchestrating microbiota-dependent epithelial metabolism and proliferation in the colon, underscoring the complexity of diet-microbiota-host interactions.
Keywords: Hypoxia; dietary fiber; intestinal stem cells; inulin; metabolism; microbiota.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
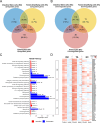

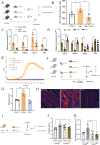


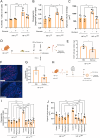
References
-
- Wiertsema SP, Van Bergenhenegouwen J, Garssen J, Knippels LMJ. The interplay between the gut microbiome and the immune system in the context of infectious diseases throughout Life and the role of Nutrition in optimizing treatment strategies. Nutrients [Internet]. 2021. [cited 2025 May 12]. 13(3):886. doi: 10.3390/nu13030886. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
