Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Different Tenecteplase Doses With Alteplase in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review With Pairwise and Network Meta-Analysis to Determine the Optimal Dose
- PMID: 40827614
- PMCID: PMC12362178
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.70756
Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Different Tenecteplase Doses With Alteplase in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review With Pairwise and Network Meta-Analysis to Determine the Optimal Dose
Abstract
Background: Tenecteplase (TNK) is a novel thrombolytic agent gaining attention as an alternative to alteplase for treating acute ischemic stroke (AIS). This meta-analysis evaluates the safety and efficacy of various TNK doses compared to alteplase, integrating recent randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and employing a frequentist network meta-analysis to identify the optimal dose while addressing existing evidence gaps.
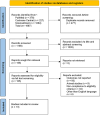
Methods: Up until December 2024, PubMed, Cochrane Central, and ScienceDirect were searched. Using Review Manager 5.4.1 for pairwise meta-analysis, the Risk Ratios (RR) with 95% Confidence Intervals (CI) were pooled under the random effects model. Additionally, R version 4.3.2 and the "netmeta" package were used to conduct a network meta-analysis for various dosages of the two thrombolytic drugs.
Results: Thirteen RCTs, pooling 9,044 patients, were included in the quantitative synthesis. TNK was associated with a statistically significant improvement in the excellent functional outcome (mRS 0-1) (RR = 1.04; 95% CI: [1.00, 1.08]; p = 0.03) compared to alteplase. No significant differences were observed between TNK and alteplase in terms of good functional outcome (mRS 0-2), poor functional outcome (mRS 5-6), major neurological improvement within 72 h, symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH), or mortality at 90 days. On network analysis, TNK 0.25 mg/kg showed significant improvement in excellent functional outcome (RR = 1.05, 95% CI: [1.01, 1.10]) and TNK 0.32 mg/kg in good functional outcome (1.30, 95% CI: [1.15, 1.48]) compared to alteplase. According to the P-score ranking, TNK 0.25 mg/kg was ranked as the best for achieving an excellent outcome (P-score = 0.86), and TNK 0.1 mg/kg as the worst (P-score = 0.16). For symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH), alteplase 0.9 mg/kg was ranked as the best (P-score = 0.71), and TNK 0.4 mg/kg as the worst (P-score = 0.17).
Conclusion: TNK (0.25-0.32 mg/kg) demonstrates superior efficacy compared to alteplase in achieving functional outcomes for AIS, while alteplase remains safer regarding sICH. Optimal dosing favors TNK 0.25 mg/kg for efficacy, but safety considerations highlight the need for individualized thrombolytic selection.
Keywords: Alteplase; dose analysis; network meta‐analysis; pairwise; stroke; tenecteplase; thrombolytic therapy.
© 2025 The Author(s). Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Figures






Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety outcomes of Tenecteplase versus Alteplase for thrombolysis of acute ischemic stroke: A meta-analysis of 9 randomized controlled trials.J Neurol Sci. 2024 Mar 15;458:122912. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2024.122912. Epub 2024 Feb 3. J Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38325064 Review.
-
Tenecteplase versus alteplase in patients with acute ischemic stroke: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Aug 8;30(1):726. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02983-9. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40775658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety among different doses of tenecteplase for acute ischemic stroke: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024 Aug;33(8):107822. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2024.107822. Epub 2024 Jun 17. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024. PMID: 38897370
-
Head-to-Head: Recombinant Human Prourokinase Versus Intravenous Thrombolytics in Acute Ischemic Stroke Within 4.5 Hours - A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2025 Jan-Dec;31:10760296251334563. doi: 10.1177/10760296251334563. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2025. PMID: 40270089 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of intravenous thrombolysis with tenecteplase versus alteplase for acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurol Sci. 2023 Sep;44(9):3005-3015. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-06801-0. Epub 2023 Apr 15. Neurol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37061572
References
-
- Bivard, A. , Zhao H., Churilov L., et al. 2022. “Comparison of Tenecteplase With Alteplase for the Early Treatment of Ischaemic Stroke in the Melbourne Mobile Stroke Unit (TASTE‐A): A Phase 2, Randomised, Open‐label Trial.” Lancet Neurology 21, no. 6: 520–527. 10.1016/S1474-4422(22)00171-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Emberson, J. , Lees K. R., Lyden P., et al. 2014. “Effect of Treatment Delay, Age, and Stroke Severity on the Effects of Intravenous Thrombolysis With Alteplase for Acute Ischaemic Stroke: A Meta‐Analysis of Individual Patient Data From Randomised Trials.” The Lancet 384, no. 9958: 1929–1935. 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60584-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

