TLR9-Driven S-Palmitoylation in Dendritic Cells Reveals Immune and Metabolic Protein Targets
- PMID: 40828036
- PMCID: PMC12363430
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.70039
TLR9-Driven S-Palmitoylation in Dendritic Cells Reveals Immune and Metabolic Protein Targets
Abstract
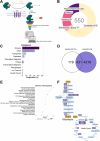
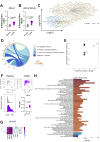
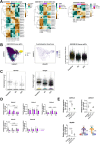
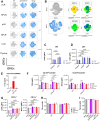
Dendritic cells (DCs) rely on Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) to detect unmethylated CpG motifs in microbial DNA, triggering essential immune responses. While the downstream signaling pathways of TLR9 activation are well characterized, their impact on S-palmitoylation is unknown. S-palmitoylation, involving the reversible attachment of palmitic acid to cysteine residues, plays a crucial role in regulating protein function and is catalyzed by the ZDHHC family of palmitoyl-acyltransferases (PATs). In this study, we investigated the S-palmitoylated proteome of bone marrow-derived GM-CSF DCs (GM-DCs) at resting and following TLR9 activation with CpGB. Using the click-chemistry-compatible analog 17-octadecynoic acid (17-ODYA) and mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomics, we characterized dynamic remodeling of S-palmitoylation in response to TLR9 activation. This included enrichment of targets involved in immune and metabolic pathways. Transcriptomic analysis of mice and human DCs revealed TLR9-driven modulation of PAT-encoding genes. Subsequently, we explored the contribution of Zdhhc9 expression to the regulation of S-palmitoylation in DCs. Using gene knockout approaches, we identified candidate protein targets potentially linked to ZDHHC9 activity. Interestingly, modulation of Zdhhc9 expression alone did not influence DC maturation, suggesting that other PATs might compensate for its activity. Together, our findings reveal a novel layer of regulation in TLR9 signaling mediated by S-palmitoylation.
Keywords: S‐palmitoylation; TLR9 signaling; dendritic cells; innate immunity.
© 2025 The Author(s). European Journal of Immunology published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

