Integrating MRI Volume and Plasma p-Tau217 for Amyloid Risk Stratification in Early-Stage Alzheimer Disease
- PMID: 40829110
- PMCID: PMC12367417
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000213954
Integrating MRI Volume and Plasma p-Tau217 for Amyloid Risk Stratification in Early-Stage Alzheimer Disease
Abstract
Background and objectives: Identifying β-amyloid (Aβ) positivity is crucial for selecting candidates for Aβ-targeted therapies in early-stage Alzheimer disease (AD). While Aβ PET is accurate, its high cost limits routine use. Plasma p-tau217 testing offers a less invasive option but also incurs additional costs. Structural brain MRI, routinely used in cognitive assessments, can identify features predictive of Aβ positivity without extra expense. We evaluated a 2-stage workflow integrating MRI-based features and plasma p-tau217 to efficiently predict Aβ PET positivity in early-stage AD.
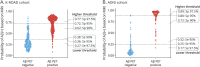
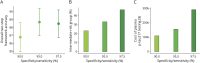
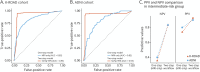
Methods: This prospective cohort study included participants with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or early Alzheimer-type dementia (ATD) from the Korea-Registries to Overcome Dementia and Accelerate Dementia Research (K-ROAD; Korea) and Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI; US) cohorts. Eligible participants had a Clinical Dementia Rating score of 0.5, along with MRI, plasma p-tau217, and Aβ PET data. A random forest classifier predicting Aβ PET positivity was developed using MRI-based brain atrophy patterns and APOE ε4 status. Participants were stratified into low-risk, intermediate-risk, and high-risk groups; plasma p-tau217 testing was performed only in intermediate-risk individuals. Outcomes included positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and overall accuracy.
Results: A total of 807 K-ROAD participants (median age 72.0 years, 58.7% female) and 230 ADNI participants (median age 70.9 years, 49.1% female) were analyzed. Using a 95% sensitivity/specificity strategy, the low-risk group demonstrated NPVs of 94.7% (91.7%-97.7%, K-ROAD) and 99.0% (97.0%-100.0%, ADNI). The high-risk group showed PPVs of 97.6% (95.9%-99.3%, K-ROAD) and 98.8% (96.5%-100.0%, ADNI). Intermediate-risk groups comprised 33.3% (K-ROAD) and 20.9% (ADNI) of participants. Plasma p-tau217 testing in intermediate-risk groups yielded PPVs of 92.5% (88.7%-96.3%, K-ROAD) and 90.0% (79.0%-100.0%, ADNI) and NPVs of 83.1% (75.0%-91.2%, K-ROAD) and 83.3% (66.1%-100.0%, ADNI). The overall workflow accuracy was 94.2% (92.6%-95.8%, K-ROAD) and 96.5% (94.1%-98.9%, ADNI).
Discussion: The 2-stage diagnostic workflow integrating MRI-based risk stratification and plasma p-tau217 testing accurately identified individuals with Aβ PET positivity in early-stage AD, substantially reducing the need for additional biomarker testing. However, the generalizability may be limited by modest incremental improvement over baseline models and limited racial and ethnic diversity.
Conflict of interest statement
S.W. Seo is a co-founder of BeauBrain Healthcare Inc. S. Park, K. Lim, and K. Kwak were employed by BeauBrain Healthcare Inc. H. Zetterberg has served at scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Acumen, Alector, Alzinova, ALZpath, Amylyx, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, Cognito Therapeutics, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, Enigma, LabCorp, Merry Life, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Optoceutics, Passage Bio, Pinteon Therapeutics, Prothena, Quanterix, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave; has given lectures sponsored by Alzecure, BioArctic, Biogen, Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Roche, and WebMD; and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program (outside submitted work). All other authors report no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. Go to
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
