Optimization and antioxidant evaluation of clean and efficient recovery of polyphenols from Phellodendron amurense waste leaves via ultrasound-assisted extraction
- PMID: 40829475
- PMCID: PMC12391693
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2025.107512
Optimization and antioxidant evaluation of clean and efficient recovery of polyphenols from Phellodendron amurense waste leaves via ultrasound-assisted extraction
Abstract
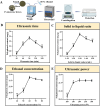
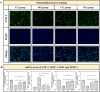
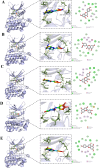
The production of edible and medicinal plants results in significant biomass waste, which can be a rich source of bioactive compounds. This study optimized the extraction of polyphenols from Phellodendron amurense leaf waste using ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE), with modeling via both response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural networks (ANN). ANN exhibited superior predictive accuracy. Under optimal UAE conditions (60 min ultrasonic time, 1:20 g/mL w/v solid-to-liquid ratio, 60 % v/v ethanol concentration, and 190 W ultrasonic power), the highest total polyphenol yield of 28.66 ± 0.07 mg GAE/g DW was achieved. The resulting extracts exhibited strong antioxidant activity in cellular assays. A total of 25 polyphenolic compounds, including luteolin, isorhamnetin, and kaempferol, were identified by liquid chromatography paired with mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), and molecular docking predicted their interaction with collagen I (COL I) as a potential antioxidant mechanism. These findings support the value-added utilization of P. amurense leaf waste and provide a foundation for its application in antioxidant nutraceuticals and plant-based pharmaceuticals.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Green chemistry; Phellodendron amurense Rupr. waste leaves; Polyphenols; Ultrasound-assisted extraction.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures








References
-
- Abulizi A., Simayi J., Nuermaimaiti M., Han M., Hailati S., Talihati Z., Maihemuti N., Nuer M., Khan N., Abudurousuli K., Dilimulati D., Nueraihemaiti N., Moore N., Zhou W., Wumaier A. Quince extract resists atherosclerosis in rats by down-regulating the EGFR/PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023;160 - PubMed
-
- Peng X., Zhao R., Yang X., Feng C., Gu H., Yang L. Separation of essential oil from fresh leaves of Phellodendron amurense rupr. by solvent-free microwave-assisted distillation with the addition of lithium salts. J. Clean. Prod. 2022;372
-
- Cai Y., Wang S., Guo W., Xie Z., Zheng Y., Cao Z., Zhou Y. Transcriptome analysis provides insights into the immune responsive pathways and genes in the head kidney of tiger grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus) fed with Spatholobus suberectus, Phellodendron amurense, or Eclipta prostrata. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018;73:100–111. - PubMed
-
- Wei Y., Bao H.Y., Liu Y., He S. Content determination of total flavonoids, total alkaloids and antioxidant activity in different processed products of Phellodendron amurense Rupr. Leaves. the Food Industry. 2022;43:161–165.
-
- Wang W., Li Q., Liu Y., Chen B. Ionic liquid-aqueous solution ultrasonic-assisted extraction of three kinds of alkaloids from Phellodendron amurense Rupr and optimize conditions use response surface. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015;24:13–18. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

