Paracrine IGFBP3 spatially coordinates IGF signaling to induce myocardial regeneration in mice
- PMID: 40829695
- PMCID: PMC12532329
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2025.08.004
Paracrine IGFBP3 spatially coordinates IGF signaling to induce myocardial regeneration in mice
Abstract
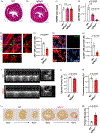
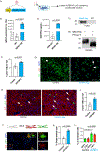
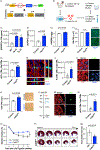
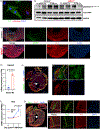
We hypothesized that the microenvironment of the regenerating neonatal mouse heart contains pro-mitotic factors. To identify non-cell-autonomous effectors of cardiomyocyte mitosis, we analyzed a transcriptomic screen of regenerating and non-regenerating hearts for differentially expressed secreted proteins. We identified IGFBP3 in this screen as a neonatal injury-associated secreted protein. IGFBP3 belongs to a family of proteins that can stabilize and sequester IGF growth factors, as well as exert IGF-independent functions. In the neonatal heart, IGFBP3 is expressed and secreted predominantly by endothelial cells following injury, notably in the border zone of the infarct. We generated loss-of-function and gain-of-function mouse models to dissect the role of IGFBP3 in myocardial regeneration. Global deletion of Igfbp3 blunted neonatal regeneration, while gain-of-function experiments using recombinant IGFBP3 or a tissue-specific ectopic Igfbp3 mouse model uncovered a pro-mitotic effect of IGFBP3 on cardiomyocytes in vitro and in the murine heart. The temporal and spatial expression of an IGFBP3 protease (PAPPA2) and IGFBP3 in the infarct zone suggests that IGFBP3 proteolysis is coordinated to locally release IGF2, which can activate an Insulin/IGF-based growth pathway to stimulate cardiomyocyte division. Collectively, our work illuminates an endothelial-cardiomyocyte crosstalk involving IGFBP3 that can mediate myocardial regeneration in the neonatal heart.
Keywords: Cardiomyocyte; Endothelium; IGF; Paracrine; Proliferation; Regeneration.
Copyright © 2025 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest All authors declare no disclosure of interest for this contribution. AI-assisted technology was not used in the preparation of this work.
Figures

References
-
- Ali SR, Lam NT, Sadek HA, 3 - cellular basis for myocardial regeneration and repair, in: Felker GM, Mann DL (Eds.), Heart Failure: A Companion to Braunwald’s Heart Disease, Fourth edition, Elsevier, Philadelphia, 2020, pp. 43–61, e3.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

