Anoikis-related genes predicts prognosis and therapeutic response in renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 40830065
- PMCID: PMC12366518
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2548042
Anoikis-related genes predicts prognosis and therapeutic response in renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Metastasis represents the primary cause of cancer-related mortality, with a high incidence observed in renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Anoikis, a specialized form of apoptosis, plays a crucial role in preventing displaced cells from adhering to new extracellular matrices (ECM), thus inhibiting their aberrant growth. Notably, cancer cells, especially metastatic ones, exhibit resistance to anoikis. However, the exact mechanisms of anoikis resistance in RCC are not well understood.
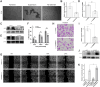
Methods: This study integrates bioinformatics, single-cell RNA sequencing and experimental validation to investigate the role of anoikis-related genes (ARG) in RCC, with a focus on MMP9. RNA-seq data from 518 RCC patients and 71 healthy controls (TCGA-KIRC) and external validation cohorts (E-MTAB-1980, GSE22541) were analyzed to construct an ARG-based prognostic model. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq, GSE159115) was used to assess tumour heterogeneity, while in vitro experiments in RCC cell lines validated MMP9's impact on anoikis resistance, migration and invasion.
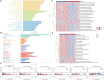
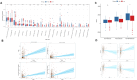
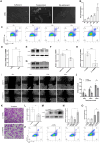
Results: We collected all RNA-seq and single-cell RNA-seq (scRNA-seq) data from multiple online databases and utilized these datasets to develop a novel ARG-based prognostic model called ARGs. Using Cox regression and machine learning, our model achieved a 5-year area under curve (AUC) of 0.79, surpassing existing models in predictive performance. Enrichment analysis revealed distinct immune and metabolic landscapes between ARGs high- and low-risk groups. At the single-cell level, tumour cells were categorized based on ARG expression, revealing heterogeneous anoikis resistance mechanisms. MMP9 was identified as a key prognostic gene (HR = 1.5, p = 0.016) associated with anoikis resistance and RCC metastasis. Functional assays confirmed that MMP9 knockdown increased anoikis by 59% and significantly reduced wound-healing migration by about 30% and transwell invasion by 50%, reinforcing its role in RCC progression.
Conclusions: Targeting anoikis-related genes, particularly MMP9, enhances anoikis sensitivity and reduces RCC invasiveness, offering a potential therapeutic strategy to mitigate metastasis and improve clinical outcomes.
Keywords: Anoikis; MMP9; metastasis; renal cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
