Modular synthesis of CF2-containing compounds with PhSO2CF2H reagent through difluoromethylene radical anion synthon strategy
- PMID: 40830095
- PMCID: PMC12365036
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62834-3
Modular synthesis of CF2-containing compounds with PhSO2CF2H reagent through difluoromethylene radical anion synthon strategy
Abstract
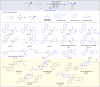
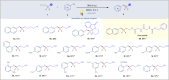
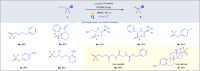
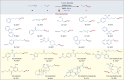
Difluoromethylene moiety has gained widespread applications in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials owing to its augmented lipophilicity and being bioisosteric to ethereal oxygen. Possessing two orthogonal reactivity modes for bridging an electrophile and a radical acceptor to give gem-difluorides (R1-CF2-R2), the efficient difluoromethylene radical anion synthon (diFRAS) has been long sought after. In this work, we successfully utilize the readily available difluoromethyl phenyl sulfone (PhSO2CF2H) to couple with electrophiles and radical acceptors, thereby enabling PhSO2CF2H to serve as a novel diFRAS in organic synthesis. The generation of radicals (•CF2R) via visible light-promoted homolytic cleavage of C-S bonds in (phenylsulfonyl)difluoromethylated derivatives (PhSO2CF2R) is the linchpin in the diFRAS strategy to construct gem-difluorides (R1-CF2-R2) with structural complexity.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Meanwell, N. A. Fluorine and fluorinated motifs in the design and application of bioisosteres for drug design. J. Med. Chem.61, 5822–5880 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Blackburn, G. M., England, D. A. & Kolkmann, F. Monofluoro- and difluoro-methylenebisphosphonic acids: isopolar analogues of pyrophosphoric acid. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 15, 930–932 (1981).
-
- Blackburn, G. M., Kent, D. E. & Kolkmann, F. The synthesis and metal binding characteristics of novel, isopolar phosphonate analogues of nucleotides. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans.1, 1119–1125 (1984).
-
- Xu, Y. et al. Structure−activity relationships of fluorinated lysophosphatidic acid analogues. J. Med. Chem.48, 3319–3327 (2005). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

