[Comparative study on effectiveness of clavicular hook plate fixation in treatment of acromioclavicular joint dislocation and distal clavicle fractures]
- PMID: 40830131
- PMCID: PMC12367411
- DOI: 10.7507/1002-1892.202504077
[Comparative study on effectiveness of clavicular hook plate fixation in treatment of acromioclavicular joint dislocation and distal clavicle fractures]
Abstract
Objective: To compare the effectiveness of clavicular hook plate fixation in the treatment of acromioclavicular joint dislocation and distal clavicle fractures.
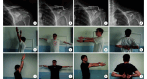
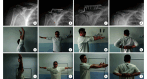
Methods: A clinical data of 90 patients, who underwent clavicular hook plate fixation between January 2014 and June 2023, was retrospectively analyzed. There were 40 patients with distal clavicle fractures (fracture group) and 50 with acromioclavicular joint dislocations (dislocation group). There was no significant difference in the baseline data of gender, age, cause of injury, side of injury, time from injury to operation, and constituent ratio of osteoporosis patients between the two groups ( P>0.05). The time to remove the internal fixators and the occurrence of complications were recorded. Before removing the internal fixator and at 3 months after removing, the visual analogue scale (VAS) score was used to evaluate the degree of pain, and the mobility of the shoulder joint in forward flexion, elevation, and abduction was measured. Before removing the internal fixators, the Constant-Murley score and the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) score were used to evaluate the function of the shoulder joint. X-ray films of the shoulder joint were taken during follow-up to observe the occurrence of subacromial osteolysis, acromioclavicular joint osteoarthritis, and distal clavicle bone atrophy. Subgroup comparison was conducted between patients with and without subacromial osteolysis in the two groups.
Results: All incisions healed by first intention in both groups. All patients were followed up 1-9 years, with a median of 5 years; the difference in follow-up time between the two groups was not significant ( P>0.05). During follow-up, subacromial osteolysis occurred in 74 cases, including 41 cases of typeⅠand 33 cases of type Ⅱ, distal clavicle bone atrophy in 15 cases, and acromioclavicular joint osteoarthritis in 8 cases. There were significant differences in the removal time of internal fixators, the incidence of bone atrophy, and the incidence of osteoarthritis between the two groups ( P<0.05). There was no significant difference in the incidence of subacromial osteolysis ( P>0.05). Before removing the internal fixators, there was no significant difference in VAS score, UCLA score, and Constant-Murley score between the two groups ( P>0.05), while there were significant differences in shoulder joint range of motion in all directions ( P<0.05). After removing the internal fixators, only the difference in elevation was significant ( P<0.05). Within the group comparison, the VAS score and mobility of shoulder joint in abduction and elevation after removing the internal fixators were significantly superior to those before removing ( P<0.05). In the fracture and dislocation groups, there was only a significant difference in plate length between the subgroup with and without subacromial osteolysis ( P<0.05), while there was no significant difference in the above other indicators ( P>0.05).
Conclusion: Clavicular hook plate is a good choice for treating acromioclavicular dislocation or distal clavicle fractures, but the incidence of subacromial osteolysis is higher, and the degree of bone resorption is more severe in fracture patients. After removal of the internal fixator, the shoulder functions significantly improve. It is recommended to remove the internal fixator as soon as possible within the allowable range of the condition.
目的: 比较锁骨钩钢板治疗肩锁关节脱位及锁骨肩峰端骨折的临床疗效。.
方法: 回顾性分析2014年1月—2023年6月符合选择标准的90例接受锁骨钩钢板内固定手术患者临床资料,其中锁骨肩峰端骨折40例(骨折组),肩锁关节脱位50例(脱位组)。两组患者性别、年龄、致伤原因、损伤侧别、受伤至手术时间、合并骨质疏松患者构成比等基线资料差异均无统计学意义( P>0.05)。记录术后取出内固定物时间;二次手术取出内固定物前以及取出术后3个月,采用疼痛视觉模拟评分(VAS)评价疼痛程度,测量肩关节前屈、上举、外展活动度;取出内固定物前采用Constant-Murley评分、美国加州大学洛杉矶分校(UCLA)评分,评价肩关节功能。随访期间复查肩关节X线片,观察肩峰下骨溶解、肩锁关节骨关节炎及锁骨肩峰端骨萎缩发生情况。并对骨折组及脱位组患者进一步分为发生与未发生骨溶解亚组进行比较。.
结果: 两组术后切口均Ⅰ期愈合。患者均获随访,随访时间1~9年,中位时间5年;两组随访时间差异无统计学意义( P>0.05)。随访期间,74例发生肩峰下骨溶解,其中Ⅰ型41例、Ⅱ型33例,15例发生锁骨肩峰端骨萎缩,8例发生肩锁关节骨关节炎。两组内固定物取出时间以及骨萎缩、骨关节炎发生率差异均有统计学意义( P<0.05),肩峰下骨溶解发生率差异无统计学意义( P>0.05)。内固定物取出前,两组VAS评分、UCLA评分及Constant-Murley评分差异均无统计学意义( P>0.05),肩关节各向活动度差异均有统计学意义( P<0.05);取出后仅肩关节上举活动度差异有统计学意义( P<0.05)。组内比较,取出后VAS评分及肩关节外展、上举活动度均优于取出前,差异有统计学意义( P<0.05)。骨折组及脱位组中,骨溶解发生亚组与未发生亚组间仅钢板长度差异有统计学意义( P<0.05),上述其他指标差异均无统计学意义( P>0.05)。.
结论: 锁骨钩钢板是治疗肩锁关节脱位及锁骨肩峰端骨折的良好选择,但肩峰下骨溶解发生率较高,且骨折患者骨溶解程度更严重。锁骨钩钢板取出后肩关节功能明显改善,建议在病情允许范围内尽早取出内固定物。.
Keywords: Distal clavicle fracture; acromioclavicular joint dislocation; clavicular hook plate; subacromial osteolysis.
Conflict of interest statement
利益冲突 在课题研究和文章撰写过程中不存在利益冲突;经费支持没有影响文章观点和对研究数据客观结果的统计分析及其报道
Figures
References
-
- Saccomanno MF, Sircana G, Cardona V, et al Biologic and synthetic ligament reconstructions achieve better functional scores compared to osteosynthesis in the treatment of acute acromioclavicular joint dislocation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(7):2175–2193. doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-06217-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li D, Qiao R, Yang N, et al Clinical analysis of the acromial height-measuring device combined with new-type clavicular hook plate and standard clavicular hook plate in the treatment of Neer type Ⅱ distal clavicle fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):448. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03338-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical