Knowledge-guided self-learning control strategy for mixed vehicle platoons with delays
- PMID: 40830216
- PMCID: PMC12365019
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62597-x
Knowledge-guided self-learning control strategy for mixed vehicle platoons with delays
Abstract
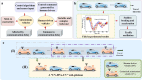
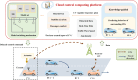
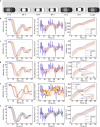
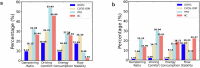
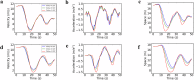
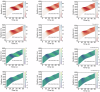
As autonomous vehicles and traditional vehicles will coexist for several decades, how to efficiently manage the mixed traffic, while enhancing road throughput, fuel consumption and traffic stability becomes a challenge. This is due to the randomness and heterogeneity of traditional vehicles interspersed among autonomous vehicles. Moreover, communication delays arising from the shared wireless communication network substantially degrade the performance of platooning control for connected autonomous vehicles. To address these challenging problems, this paper proposes a knowledge-guided self-learning mixed platoon control strategy. Firstly, the proposed strategy extracts key features of the continuous and aggregated behavior of traditional vehicles, such as desired time-varying time gap and standstill spacing, by integrating knowledge from the kinematic wave model and Newell's car-following model. This helps autonomous vehicles predict traditional vehicles' trajectories. Secondly, to tackle delayed current state information, the study incorporates previous control instructions into the state representation of the soft actor-critic algorithm. Simulations show the proposed strategy outperforms existing methods in traffic stability, passenger comfort, energy consumption cost and traffic oscillation dampening, with a zero collision rate in vehicle merging and diverging scenarios. The framework provides a generalizable and scalable solution for the development and adoption of connected autonomous vehicle systems.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

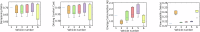



Similar articles
-
Integrated neural network framework for multi-object detection and recognition using UAV imagery.Front Neurorobot. 2025 Jul 30;19:1643011. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2025.1643011. eCollection 2025. Front Neurorobot. 2025. PMID: 40809070 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Vision screening of older drivers for preventing road traffic injuries and fatalities.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Feb 21;2014(2):CD006252. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006252.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24563119 Free PMC article.
-
Estimates of emissions from hydrogen transportation fueling infrastructure and vehicles.J Air Waste Manag Assoc. 2025 Jul;75(7):559-590. doi: 10.1080/10962247.2025.2495811. Epub 2025 Jun 16. J Air Waste Manag Assoc. 2025. PMID: 40327627 Review.
References
-
- Zhou, Y., Lin, Y., Ahn, S., Wang, P. & Wang, X. Platoon trajectory completion in a mixed traffic environment under sparse observation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst.23, 16217–16226 (2022).
-
- Antonakaki, A., Oikonomou, M. G., Garefalakis, T. & Yannis, G. Driving automation systems penetration and traffic safety: Implications for infrastructure design and policy. Infrastructures9, 234 (2024).
-
- Milakis, D., Snelder, M., Van Arem, B., Van Wee, B. & Homem De Almeida Correia, G. Development and Transport Implications of Automated Vehicles in the Netherlands: Scenarios for 2030 and 2050. Eur. J. Transp. Infrastruct. Res.17, 63–85 (2017).
-
- Li, T., Guo, F., Krishnan, R., Sivakumar, A. & Polak, J. Right-of-way reallocation for mixed flow of autonomous vehicles and human driven vehicles. Transp. Res. C Emerg. Technol.115, 102630 (2020).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

