Genetic determinants of pOXA-48 plasmid maintenance and propagation in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 40830342
- PMCID: PMC12365149
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62404-7
Genetic determinants of pOXA-48 plasmid maintenance and propagation in Escherichia coli
Abstract
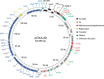
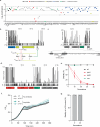
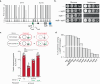
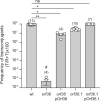
Conjugative plasmids are the main drivers of antibiotic resistance dissemination contributing to the emergence and extensive spread of multidrug resistance clinical bacterial pathogens. pOXA-48 plasmids, belonging to the IncL group, emerge as the primary vehicle for carbapenem resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. Despite the problematic prevalence of pOXA-48, most research focus on epidemiology and genomics, leaving gaps in our understanding of the mechanisms behind its propagation. In this study, we use a transposon sequencing approach to identify genetic elements critical for plasmid stability, replication, and conjugative transfer. Our results identify a novel type I toxin-antitoxin system, uncharacterized essential maintenance factors, and components of the type IV secretion system and regulatory elements crucial for conjugation. This study advances our understanding of pOXA-48 biology, providing key insights into the genetic factors underlying its successful maintenance and spread in bacterial populations.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ANR-22-CE35-0017/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- ANR-19CE12-0001/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- ANR-22-CE35-0017/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- ANR-22-CE12-0032/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- EQU202103012587/Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (Foundation for Medical Research in France)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

