Exploring the effect of pre-clinical Alzheimer's disease on blood pressure using Mendelian randomisation and parental dementia as an instrumental variable in UK Biobank
- PMID: 40830462
- PMCID: PMC12366137
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-025-04295-5
Exploring the effect of pre-clinical Alzheimer's disease on blood pressure using Mendelian randomisation and parental dementia as an instrumental variable in UK Biobank
Abstract
Background: Evidence suggests there may be a bidirectional relationship between high blood pressure (BP) and Alzheimer's disease (AD). It is hypothesised that this is due to cerebral changes during pre-clinical AD that cause elevation of systemic BP. We aimed to test this by exploring the effect of risk of pre-clinical AD on blood pressure.
Methods: We used data from the UK Biobank, including adults without prevalent or incident (within first 5 years of follow-up) clinical AD (N = 501,420, mean age 56.6, SD 8 years). We used two instrumental variables, an age-weighted parental dementia instrument score and a participant genetic instrument score, that are vulnerable to differing biases, to instrument risk of pre-clinical AD (the exposure). We tested the association of both instrument scores with systolic BP (SBP), diastolic BP (DBP), and hypertension. Sensitivity analyses were undertaken to explore different biases.
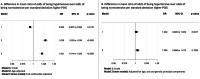
Results: Both the higher parental dementia instrument and participant genetic instrument score were associated with higher mean SBP (difference in mean SBP mmHg per 1SD higher score: 0.12, 95% CI 0.06 to 0.17, p < 0.0001, and 0.07, 95% CI 0.00 to 0.13, p=0.037, respectively) but not DBP. Sensitivity analyses were largely consistent with these findings. CONCLUSIONS: Our findings provide preliminary evidence that pre-clinical AD increases SBP. Further research is required to determine whether this increase in SBP is due to increased cerebrovascular resistance as a result of pre-clinical AD. Obtaining a better understanding of the changing relationship with BP at different stages of AD may enable effective optimisation and targeting of therapies.
Keywords: Blood pressure; Human population; Instrumental variables; Pre-clinical Alzheimer’s disease; Prospective cohort.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All participants had provided written informed consent, approved by the Northwest Multicentre Research Ethics Committee. As data were deidentified, this study did not require additional ethics committee approval. Consent for publication: Data used in this study are entirely unidentifiable and no details on individuals are reported within the manuscript. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Genetic Complexities of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease, Blood Pressure, and Dementia.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 May 1;7(5):e2412824. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.12824. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 38776079 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacotherapies for sleep disturbances in dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 16;11(11):CD009178. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009178.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 15;11:CD009178. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009178.pub4. PMID: 27851868 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Regional cerebral blood flow single photon emission computed tomography for detection of Frontotemporal dementia in people with suspected dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jun 23;2015(6):CD010896. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010896.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26102272 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a gluten-reduced or gluten-free diet for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 24;2(2):CD013556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35199850 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

