Enhanced meropenem activity and stability following load in Polyvinyl alcohol nanofiber scaffolds with sitagliptin as quorum sensing inhibitor on Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 40830972
- PMCID: PMC12366121
- DOI: 10.1186/s13036-025-00549-1
Enhanced meropenem activity and stability following load in Polyvinyl alcohol nanofiber scaffolds with sitagliptin as quorum sensing inhibitor on Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
Background: The increasing resistance of bacteria to conventional antibiotics poses a significant health challenge. Innovative strategies, such as combining antibiotics with agents like quorum sensing inhibitors (QSIs), have been developed to combat this issue. QSIs enhance antibiotic efficacy without inhibiting bacterial growth, minimizing the risk of resistance.
Aims: Evaluate the combined effect of Sitagliptin (STG) as a QSI with Meropenem (MER), fabricate drug-loaded Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) nanofibers, and investigate their antimicrobial activity against standard Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PAO1) and carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa (CRPA).
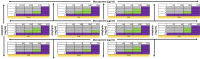
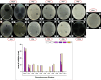
Methods: The combinatorial effect was assessed using a checkerboard assay. PVA/STG, PVA/MER, and PVA/STG/MER nanofibers were fabricated with varying concentrations of STG (2, 4, 8 mg/mL) and MER (5, 7, 9 mg/mL) via electrospinning. Characterization was performed using FTIR, XRD, and SEM techniques.
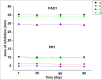
Results: STG significantly reduced the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of MER. The 1:2 STG to MER ratio exhibited the highest antimicrobial activity, achieving a comparable zone of inhibition to the highest concentration of MER while utilizing nearly half the amount of MER. The stability of the loaded scaffolds was maintained over three months at 2-8 °C.
Conclusions: Our results underscore the successful fabrication of nanofiber scaffolds and the effectiveness of STG and MER-loaded nanofibers as promising wound dressings for cutaneous P. aeruginosa infections. This study highlights the potential of our innovative nanofiber system to enhance treatment efficacy against multidrug-resistant bacteria, offering a personalized and rapid response wound dressing solution for medical professionals. Ultimately, it shows promise to improve patient recovery and quality of life while minimizing systemic side effects.
Keywords: Antibacterial activity; Electrospinner; Meropenem; Nanofibers; Sitagliptin.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable, no animal was used in this study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering of a decellularized bovine skin coated with antibiotics-loaded electrospun fibers with synergistic antibacterial activity for the treatment of infectious wounds.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2024 Apr;121(4):1453-1464. doi: 10.1002/bit.28659. Epub 2024 Jan 17. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2024. PMID: 38234099
-
Cefadroxil-Mupirocin Integrated Electrospun Nanofiber Films for Burn Wound Therapy.Curr Drug Deliv. 2025 Jun 18. doi: 10.2174/0115672018374558250607134659. Online ahead of print. Curr Drug Deliv. 2025. PMID: 40539348
-
Antimicrobial dressings for the prevention of catheter-related infections in newborn infants with central venous catheters.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 23;3(3):CD011082. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011082.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27007217 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morales S, Gallego MA, Vanegas JM, Jiménez JN. Detection of carbapenem resistance genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates with several phenotypic susceptibility profiles, Ces Medicina. 2018;32(3):203–214. 10.21615/cesmedicina.32.3.2
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

