From tradition to transformation: evolving models of care in clinical genetics
- PMID: 40831355
- PMCID: PMC12594115
- DOI: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000001502
From tradition to transformation: evolving models of care in clinical genetics
Abstract
Purpose of review: The integration of genomics into mainstream healthcare is transforming clinical genetics into a foundational component of modern medicine. This review explores the evolution of clinical genetics service delivery, highlighting evolving models of care designed to meet rising demand, improve access, and ensure equitable, patient-centered genomic care.
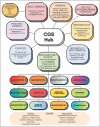
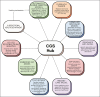
Recent findings: Key models of care discussed include multidisciplinary team approaches, embedded genetic counselors, advanced practice providers, upskilled non-genetics specialists, laboratory-based genetics clinicians, primary care providers of genetic healthcare and automated/patient-directed models. Educational needs, funding and adjuncts such as genetic assistants, collaborative telegenetics, and digital tools are also discussed for their role in supporting sustainable implementation.
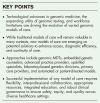
Summary: We recommend health organizations develop a roadmap for genomic medicine through creation of a genomic medicine governance framework, assessment of workforce capacity, definition of patient cohorts, and reviewing their infrastructure readiness. No single model of care is suitable for every context. By clearly defining needs, acknowledging limitations, and identifying potential risks, organizations can select the most appropriate models to address both current and future requirements. As genomics becomes increasingly embedded in routine care, we believe a coordinated, evidence-based approach is essential to ensure well tolerated, effective, accessible, equitable, and sustainable delivery of genomic medicine across diverse healthcare settings.
Keywords: clinical genetics; genetics workforce; genomics MDT; genomics models of care; mainstreaming genomics.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Sukenik-Halevy R, Ludman MD, Ben-Shachar S, Raas-Rothschild A. The time-consuming demands of the practice of medical genetics in the era of advanced genomic testing. Genet Med 2016; 18:372–377. - PubMed
-
- Fennell AP, Hunter MF, Corboy GP. The changing face of clinical genetics service delivery in the era of genomics: a framework for monitoring service delivery and data from a comprehensive metropolitan general genetics service. Genet Med 2020; 22:210–218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

