The parallel mediating role of time and financial resources in achievement motivation and non-credential learning
- PMID: 40831485
- PMCID: PMC12359079
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1579281
The parallel mediating role of time and financial resources in achievement motivation and non-credential learning
Abstract
Introduction: The surge in non-degree credentials, such as micro-credentials and MOOC, in China is being driven by evolving labor market needs and the growing demand for specialized skills. Participation in such programs is influenced by various internal factors, particularly achievement motivation, as well as external factors like time management and financial resources. Yet, the impact of these factors on willingness to participate remains unexplored.
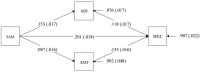
Methods: This study examines the relationship between achievement motivation and engagement in non-degree credential education, focusing on the mediating roles of self-directed learning time and financial capability. Data from 3,397 Chinese college students aged 18-22 were analyzed using a parallel mediation model. Structural equation modeling was employed to analysis the data.
Results: The findings reveal that both learning time and financial resources significantly mediate this relationship, each with distinct levels of influence. Students with higher achievement motivation tend to invest more time and money in non-degree credential learning, thereby enhancing their likelihood of participation.
Discussion: These results highlight the critical roles of time management and financial capacity in shaping students' involvement in non-degree credentials, offering valuable insights for educational policymakers and institutions seeking to enhance accessibility and support for non-degree credential programs in higher education.
Keywords: achievement motivation; financial resources; non-degree credentials courses; parallel mediation; self-directed learning time.
Copyright © 2025 Cao, Tian, Hu and Kou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alvarez Sainz M., Ferrero A. M., Ugidos A. (2019). Time management: skills to learn and put into practice. Educ. Train. 61, 635–648. doi: 10.1108/ET-01-2018-0027 - DOI
-
- Banahan L., Mullendore R. (2014). Navigating the first college year. A guide for parents and families. National Resource Center for the first-year experience and students in transition (Columbia: University of South Carolina; ).
-
- Dwijuliani R., Rijanto T., Nurlaela L., Basuki I. (2021). Increasing student achievement motivation during online learning activities. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1810:12072. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1810/1/012072 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources