Concentration-dependent effects of boron fertilizer on growth, yield, and quality of buckwheat
- PMID: 40831719
- PMCID: PMC12358468
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1548792
Concentration-dependent effects of boron fertilizer on growth, yield, and quality of buckwheat
Abstract
Introduction: Boron is an essential trace element for plant growth and development, playing a critical role in flowering, fruit setting, nutrient transport, and stress resistance in crops. Buckwheat is an important coarse grain crop, and its yield and quality are easily affected by boron nutritional status.
Methods: In order to identify the optimal concentration of boron fertilizer to maximize growth and yield of buckwheat, pot experiments and field trials were carried out at different mass concentrations of boron fertilizer solution: 0, 12, 24, 48, and 72 mg/L.
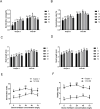
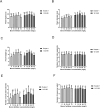
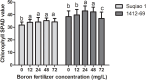
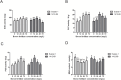
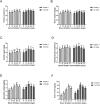
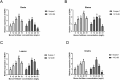
Results: The results showed that 48 mg/L boron fertilizer solution promoted seed germination and seedling growth of Suqiao 1, whereas 24 mg/L boron fertilizer solution had the best effect on seed germination and seedling growth of 1412-69. Moreover, the levels of activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and peroxidase (POD) of Suqiao 1 seedlings were highest under the 48 mg/L boron fertilizer treatment, and those in 1412-69 were highest under the 24 mg/L treatment. The highest grain yield and grain quality of Suqiao 1 were found at a boron concentration of 48 mg/L, whereas grain yield and quality of 1412-69 were maximized at a concentration of 24 mg/L.
Discussion: In summary, boron fertilizer solutions at optimal concentrations can effectively stimulate buckwheat seed germination and seedling growth and thus enhance buckwheat yield.
Keywords: boron fertilizer; buckwheat; quality; seed germination; seedling growth; yield.
Copyright © 2025 Jiang, Wang, Liu, Wang, Chang, Cai, Yu and Chang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Performance of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) in response to variable sowing time in low altitude conditions.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Aug 11;25(1):1066. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-07090-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40790172 Free PMC article.
-
By promoting growth and development, castor bean meal biofertilizer improves the yield and quality of Tartary buckwheat and indirectly improves the growth and development of Tartary buckwheat sprouts.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jun 5;16:1584608. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1584608. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40538872 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium and silicon nanofertilizers improved morphological attributes and fatty acid composition in olive; an insight to synergistic interaction between these elements.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jul 31;25(1):997. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-07027-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40745585 Free PMC article.
-
The quantity, quality and findings of network meta-analyses evaluating the effectiveness of GLP-1 RAs for weight loss: a scoping review.Health Technol Assess. 2025 Jun 25:1-73. doi: 10.3310/SKHT8119. Online ahead of print. Health Technol Assess. 2025. PMID: 40580049 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arrobas M., Raimundo S., Conceição N., Moutinho-Pereira J., Correia C. M., Rodrigues M. (2023). On sandy, boron-poor soils, liming induced severe boron deficiency and drastically reduced the dry matter yield of young olive trees. Plants (Basel) 12, 4161. doi: 10.3390/plants12244161, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen X. F., Chen H. H., Huang W. L., Huang W. T., Huang Z. R., Yang L. T., et al. (2024). Boron reduced copper excess-induced oxidative damage in Citrus sinensis by modulating reactive oxygen species and methylglyoxal formation and their detoxification systems. Antioxidants (Basel) 13, 268. doi: 10.3390/antiox13030268, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- da Silva Liber Lopes P. M., Campos C. N. S., Teodoro P. E., Costa M. G., de Souza Júnior J. P., de Mello Prado R. (2023). The synergistic effects of soil-applied boron and foliar-applied silicon on cotton fiber quality and yield. BMC Plant Biol. 23, 520. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04542-y, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

