IR808-ATIPA: A Dual-Function Agent for Enhanced Computed Tomography Imaging and Radiotherapy Sensitization in Cervical Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 40831788
- PMCID: PMC12358750
- DOI: 10.34133/bmr.0222
IR808-ATIPA: A Dual-Function Agent for Enhanced Computed Tomography Imaging and Radiotherapy Sensitization in Cervical Cancer Treatment
Abstract
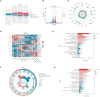
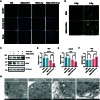
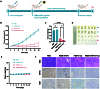
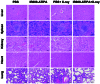
Radiotherapy is pivotal in localized cancer treatment, yet balancing therapeutic efficacy with collateral tissue damage remains challenging. Conventional iodinated contrast agents, limited by rapid metabolism and short imaging windows, hinder precise radiotherapy planning. We developed IR808-ATIPA, a tumor microenvironment-responsive iodine-based compound integrating computed tomography (CT) imaging and radiosensitization. Synthesized by covalently linking IR808 and ATIPA, IR808-ATIPA leverages iodine's x-ray attenuation for high-contrast imaging while enhancing radiation dose deposition in cervical cancer. Unlike conventional agents, its prolonged tumor retention improves imaging accuracy and therapeutic targeting. Evaluations in HeLa tumor-bearing nude mice demonstrated superior in vitro/in vivo imaging performance and sustained tumor accumulation. RNA sequencing revealed that IR808-ATIPA enhances radiotherapy efficacy by activating the ferroptosis pathway via increased reactive oxygen species production and amplified x-ray absorption. Safety assessments confirmed no notable toxicity to major organs. IR808-ATIPA functions dually as a CT contrast agent for precise tumor delineation and a radiosensitizer promoting ferroptosis-mediated radiotherapy enhancement. Its extended intratumoral retention enables targeted therapy, minimizing off-target effects. These findings highlight IR808-ATIPA as a promising theranostic agent, bridging imaging-guided precision and therapeutic efficacy to advance personalized cancer treatment.
Copyright © 2025 Kejin Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Engineered multifunctional nanoparticles for enhanced radiation therapy: three-in-one approach for cancer treatment.Mol Cancer. 2025 Mar 6;24(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02266-1. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40050802 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Medicine Computed Tomography Physics.2025 Apr 27. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Apr 27. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 35881729 Free Books & Documents.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound using SonoVue® (sulphur hexafluoride microbubbles) compared with contrast-enhanced computed tomography and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for the characterisation of focal liver lesions and detection of liver metastases: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2013 Apr;17(16):1-243. doi: 10.3310/hta17160. Health Technol Assess. 2013. PMID: 23611316 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gao Y, Fan X, Hua C, Zheng H, Cui Y, Li Y, Wu K. Failure patterns for thymic carcinoma with completed resection and postoperative radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2023;178: Article 109438. - PubMed
-
- Liu ZC, Zeng KH, Gu ZB, Chen RP, Luo YJ, Tang LQ, Zhu KB, Liu Y, Sun XS, Zeng L. Comparison of induction chemotherapy combined with concurrent chemoradiotherapy versus concurrent chemoradiotherapy alone in lymph-node-stage III nasopharyngeal carcinoma based on propensity score-matching. Radiother Oncol. 2023;178: Article 109421. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Mu X, He H, Zhang XD. Cancer radiosensitizers. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018;39(1):24–48. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

