Impact of remnant cholesterol on short-term mortality in acute decompensated heart failure: cohort study evidence from Jiangxi, China
- PMID: 40831947
- PMCID: PMC12358261
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1624112
Impact of remnant cholesterol on short-term mortality in acute decompensated heart failure: cohort study evidence from Jiangxi, China
Abstract
Introduction: Remnant cholesterol (RC), a highly atherogenic lipid component, has been strongly implicated in the pathogenesis and adverse clinical outcomes of numerous cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. However, its impact on short-term prognosis in patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) remains to be elucidated.
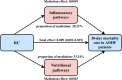
Methods: This study enrolled 2,365 patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) admitted to Jiangxi Provincial People's Hospital from 2018 to 2024. Participants were stratified into quartiles based on RC. The primary outcome was 30-day all-cause mortality. Multivariable-adjusted Cox regression and restricted cubic spline regression were employed to analyze the association between RC and 30-day mortality in ADHF patients. Additionally, exploratory mediation analyses were performed to assess potential mediating roles of inflammation, oxidative stress, and nutritional factors in this relationship.
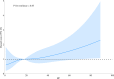
Results: During the 30-day follow-up period, 151 deaths were recorded. Mortality was significantly higher in the highest RC quartile compared to the other three groups (Q1:4.41% vs Q2:5.85% vs Q3:5.93% vs Q4:9.18%). After full adjustment for potential confounders, RC demonstrated a significant linear positive association with 30-day mortality in ADHF patients [Hazard ratio: 1.16 (1.05, 1.28)]. Compared with those in the lowest quartile, patients in the highest RC quartile had a 76% increased risk of 30-day mortality. Further subgroup analyses demonstrated that ADHF patients with comorbid hypertension, coronary heart disease, and reduced ejection fraction had a significantly higher 30-day mortality risk than those without these conditions.
Discussion: This Chinese cohort study reveals a dose-dependent relationship between RC and 30-day mortality in ADHF patients, particularly exacerbated in those with hypertension, coronary heart disease, or reduced ejection fraction.
Keywords: acute decompensated heart failure; cohort study; longitudinal study; mortality; remnant cholesterol.
Copyright © 2025 Jian, Jiang, Lu, He, Xie, Zhang, Wang, Lu, Xiong, Wu, Xie, Sheng, Xie, Liu, Wang and Zou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Independent and combined associations of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol-modified triglyceride-glucose index with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with acute decompensated heart failure.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 29;16:1629066. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1629066. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40801032 Free PMC article.
-
Aggregate index of systemic inflammation as a novel prognostic biomarker in Chinese patients with acute decompensated heart failure: a population-based real-world study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Aug 13;16:1627821. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1627821. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40881126 Free PMC article.
-
BUN-to-ALB ratio as an effective predictor of 30 day mortality in ADHF patients in eastern China.ESC Heart Fail. 2025 Aug;12(4):2540-2551. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.15289. Epub 2025 Apr 1. ESC Heart Fail. 2025. PMID: 40170368 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) for the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular diseases.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 May 6;5(5):CD013729. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013729.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40326569 Review.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
References
-
- Chinese Society of Cardiology. Chinese Medical Association. Chinese College of Cardiovascular Physician. Chinese Heart Failure Association of Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Cardiology . Chinese guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of heart failure 2024. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. (2024) 52:235–75. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112148-20231101-00405, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- GBD 2021 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators . Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet. (2024) 403:2133–61. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00757-8, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

