Research trends and topics on sepsis immunosuppression: a bibliometric and visual analysis of global research from 2004 to 2024
- PMID: 40832104
- PMCID: PMC12358459
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1615753
Research trends and topics on sepsis immunosuppression: a bibliometric and visual analysis of global research from 2004 to 2024
Abstract
Background: Sepsis, a condition characterized by critical organ impairment resulting from dysregulated response to infection, remains a leading cause of mortality globally. Immunosuppression significantly dictates the clinical trajectory and ultimate prognosis in sepsis. Research on sepsis-related immunosuppression has gained substantial attention in recent years. However, a comprehensive and objective analysis of the current state of research remains scarce. This study employs bibliometric techniques and knowledge mapping to provide a visual analysis of trends and developments in sepsis immunosuppression, offering a systematic overview for researchers in the field.
Objectives: This study aims to: (1) Quantitatively characterize global publication trends, key contributors (countries/institutions/journals/authors), and collaborative networks in sepsis immunosuppression research (2004-2024); (2) Identify current hotspots and future directions in this field.
Materials and methods: Articles and reviews related to sepsis immunosuppression were sourced from the Web of Science Core Collection via subject-specific searches. Bibliometric analyses were executed using Excel 365, CiteSpace, VOSviewer, and Bibliometrix (R-Studio's R-Tool).
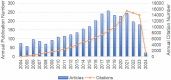
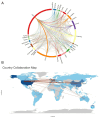
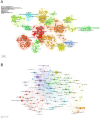
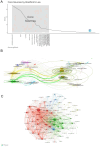
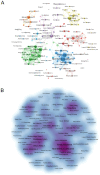
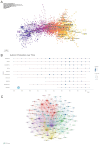
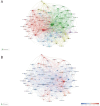
Results: From January 1, 2004, to March 22, 2024, 3,082 articles on sepsis immunosuppression authored by 16,545 individuals across 116 institutions from 30 countries were identified. Collaborative network analysis highlights the United States as the leading contributor, with key institutions including the University of Florida and Washington University. Strong international collaboration is evident, particularly between the United States and China, as well as the United States and Germany. Frontiers in Immunology emerged as the most prolific journal, while Journal of Immunology garnered the highest co-citation frequency. Guillaume Monneret has published the greatest number of relevant articles, while Richard S. Hotchkiss is the most frequently co-cited author. The research predominantly focuses on immunology, molecular biology, and clinical treatments. Keyword analysis suggests that immune cells, cell death, and personalized clinical treatments are emerging research hotspots in the field.
Conclusion: This bibliometric analysis maps evolving trends and forecasts emerging hotspots in sepsis immunosuppression research, providing direction for future studies.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis; clinical treatment; immunoparalysis; immunosuppression; sepsis.
Copyright © 2025 Yin, Wan, Chen, Li, Liu, Luo, Li, Li and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Research status, hotspots and perspectives of artificial intelligence applied to pain management: a bibliometric and visual analysis.Updates Surg. 2025 Jun 28. doi: 10.1007/s13304-025-02296-w. Online ahead of print. Updates Surg. 2025. PMID: 40580377
-
Application of non-invasive imaging in myocardial infarction: a bibliometric analysis from January 2003 to December 2022.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 Jul 1;15(7):6340-6359. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-878. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 40727351 Free PMC article.
-
Global research trends and hotspots in prognostic prediction models for pancreatic cancer: a bibliometric analysis.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 10;15:1588735. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1588735. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40708943 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric analysis of research trends in mesenchymal stem cell therapy for neonatal bronchopulmonary dysplasia: 2004-2024.Front Pediatr. 2025 Jun 3;13:1558301. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1558301. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40530182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bibliometric and visualized analysis of global distribution and research frontiers in tumor immune escape.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 5;16:1586120. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1586120. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40539064 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

