This is a preprint.
Novel Predictive Spatial Biomarker in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma: The Diversity of Niches Unlocking Treatment Sensitivity (DONUTS)
- PMID: 40832222
- PMCID: PMC12363902
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.08.13.665980
Novel Predictive Spatial Biomarker in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma: The Diversity of Niches Unlocking Treatment Sensitivity (DONUTS)
Abstract
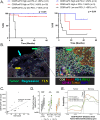
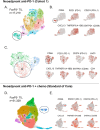
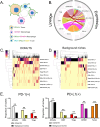
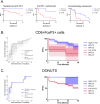
Probabilistic spatial modelling techniques developed on large-scale tumor-immune Atlases (~35M individually mapped cells; 50,000 high power fields) were used to characterize predictive features of treatment-responsive lung cancer. We identified CD8+FoxP3+ cell density as a robust pre-treatment biomarker for outcomes across disease stages and therapy types. In parallel, single-cell RNAseq studies of CD8+FoxP3+ T-cells revealed an activated, early effector phenotype, substantiating an anti-tumor role, and contrasting with CD4+FoxP3+ T-regulatory cells. A spatial biomarker was developed using an empirical probabilistic model to define the immediate cell neighbors or niche surrounding CD8+FoxP3+ cells and proximity to the tumor-stromal boundary. The resultant 'Diversity of Niches Unlocking Treatment Sensitivity (DONUTS)' are more prevalent than the CD8+FoxP3+ cells themselves, mitigating sampling error in small biopsies. Further, the DONUTS only require four markers, are additive to PD-L1, and associate with tertiary lymphoid structure counts. Taken together, the DONUTS represent a next-generation predictive biomarker poised for clinical implementation.
Keywords: AstroPath; CD8+FoxP3+; NSCLC; PD-1; biomarker; immunotherapy; lung cancer; neighborhood; pathology; spatial.
Conflict of interest statement
D.M.P. reports other support from Aduro Biotech, Amgen, Bayer, Camden Partners, DNAtrix, Dracen, Dynavax, FLX Bio, Immunomic, Janssen, Merck, Rock Springs Capital, Potenza, Tizona, Trieza, and WindMil during the conduct of the study; grants from Astra Zeneca, Medimmune/Amplimmune, and Compugen; grants and other support from Bristol-Myers Squibb, ERvaxx, and Potenza; personal fees from AbbVie, Avidity Nanomedicines, ImaginAb, Immunocore, and Merck; and personal fees and nonfinancial support from Five Prime Therapeutics and Dragonfly Therapeutics. J.S.D. reports consulting for NextPoint; J.M.T. reports grants and consulting from Bristol-Myers Squibb and consulting for Merck, Astra Zeneca, Moderna, Roche, NextPoint, Elephas, Regeneron, and Compugen outside the submitted work; J.M.T. and A.S.S. report equipment, reagents, and stock options from Akoya Biosciences and a patent pending related to image processing of mIF/IHC images. J.M.T., A.S.S., B.F.G., J.S.R., L.L.E. report a patent pending related to spatial predictors of response to therapy which has been licensed by Quanterix. J.M.T., A.S.S, and J.R. also report institutional grant funding from Quanterix. K.N.S. has received travel support/honoraria from Illumina, Inc., receives research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Anara, and Astra Zeneca, and owns founder’s equity in Clasp Therapeutics, LLC. P.M.F. receives research support from AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, and Kyowa, and has been a consultant for AstraZeneca, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daichii Sankyo, and Janssen and serves on a data safety and monitoring board for Polaris. J.E.C. reports trial funding provided to her institution by Astra Zeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Genentech, Lilly, Merck, BioNTech; and consulting fees from Astra Zeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Genentech/Roche, Guardant Health, Lilly, Merck, Natera, Nuvation Bio.
Figures


References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
