This is a preprint.
Profibrotic monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages as a biomarker and therapeutic target in systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease
- PMID: 40832362
- PMCID: PMC12363918
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.08.07.669006
Profibrotic monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages as a biomarker and therapeutic target in systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease
Abstract
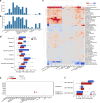
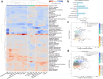
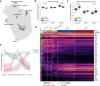
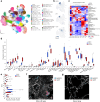
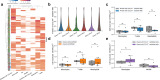
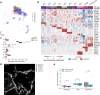
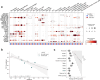
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is present in over 60% of patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) and is the leading cause of SSc-related deaths. Profibrotic monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages (MoAM) play a causal role in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis in animal models where their persistence in the niche requires signaling through Colony Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor (CSF1R). We hypothesized that the presence and proportion of MoAM in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid from patients with SSc-ILD may be a biomarker of ILD severity. To test this hypothesis, we analyzed BAL fluid from 9 prospectively enrolled patients with SSc-ILD and 13 healthy controls using flow cytometry and single-cell RNA sequencing. Patients with SSc-ILD had more MoAM and interstitial macrophages in BAL fluid than healthy controls, and their abundance was associated with lung fibrosis severity. We identified changes in the MoAM transcriptome as a function of treatment with mycophenolate, an effective therapy for SSc-ILD. In SSc-ILD lung explants, spatial transcriptomics identified an expanded population of interstitial macrophages spilling into the alveolar space. Our findings suggest that the proportion of profibrotic MoAM and interstitial macrophages in BAL fluid may serve as a biomarker of SSc-ILD and credential them as possible targets for therapy.
Figures

References
-
- Denton CP, Wells AU, Coghlan JG. Major lung complications of systemic sclerosis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018. Sep; 14(9):511–527. - PubMed
-
- George PM, Spagnolo P, Kreuter M, Altinisik G, Bonifazi M, Martinez FJ, Molyneaux PL, Renzoni EA, Richeldi L, Tomassetti S, Valenzuela C, Vancheri C, Varone F, Cottin V, Costabel U. Progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease: clinical uncertainties, consensus recommendations, and research priorities. Lancet Respir Med. 2020. Sep; 8(9):925–934. - PubMed
-
- Misharin AV, Morales-Nebreda L, Reyfman PA, Cuda CM, Walter JM, McQuattie-Pimentel AC, Chen CI, Anekalla KR, Joshi N, Williams KJN, Abdala-Valencia H, Yacoub TJ, Chi M, Chiu S, Gonzalez-Gonzalez FJ, Gates K, Lam AP, Nicholson TT, Homan PJ, Soberanes S, Dominguez S, Morgan VK, Saber R, Shaffer A, Hinchcliff M, Marshall SA, Bharat A, Berdnikovs S, Bhorade SM, Bartom ET, Morimoto RI, Balch WE, Sznajder JI, Chandel NS, Mutlu GM, Jain M, Gottardi CJ, Singer BD, Ridge KM, Bagheri N, Shilatifard A, Budinger GRS, Perlman H. Monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages drive lung fibrosis and persist in the lung over the life span. J Exp Med. 2017. Aug; 214(8):2387–2404. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- R01 AR080513/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI181102/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR073270/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG075423/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL163611/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD011996/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL146943/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI135964/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL154998/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL145478/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147575/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL169188/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134800/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL176632/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 CX001777/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- R01 ES034350/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES027574/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG049665/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL153312/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AG079754/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL158139/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147290/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- L30 HL149048/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM129312/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
