Green light modulates disease resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana against Pseudomonas syringae pv . tomato
- PMID: 40833277
- PMCID: PMC12377085
- DOI: 10.1080/15592324.2025.2546465
Green light modulates disease resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana against Pseudomonas syringae pv . tomato
Abstract
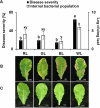
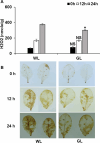
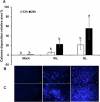
Light plays a pivotal role in regulating plant physiological processes. However, the influence of specific light wavelengths on plant defense to pathogen infection remains insufficiently explored. We investigated the role of different light wavelengths, with a particular focus on green light (GL), in modulating disease responses and signaling in Arabidopsis. We pretreated Arabidopsis Col-0 plants with various light wavelengths before challenging them with Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 (PstDC3000). GL at an intensity of 100 µmol m-2 s-1 significantly suppressed disease incidence compared to white light (WL). GL upregulated the expression of key defense-related genes, including COI1, JAR1, PDF1.2, and PAD4, compared to WL. Furthermore, GL promoted callose deposition and reduced H2O2 production relative to the WL treatment. Jasmonic acid (JA)-deficient mutants (∆Jar1 and ∆Coi1) exhibited heightened disease severity under GL treatment compared with that of Col-0, underscoring the central role of the JA pathway in GL-mediated defense responses. These results indicate that GL functions as a crucial modulator of the defense response in Arabidopsis, offering new insights into the relationship between light quality and plant immunity. However, further research is required to elucidate the precise perception mechanisms and signaling networks involved in GL-mediated defense responses.
Keywords: Green light; jasmonic acid; light; photoreceptor; resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures

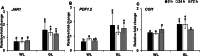


Similar articles
-
Chitosan Oligosaccharide Induces Resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 in Arabidopsis thaliana by Activating Both Salicylic Acid- and Jasmonic Acid-Mediated Pathways.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2018 Dec;31(12):1271-1279. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-03-18-0071-R. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2018. PMID: 29869942
-
A homeobox transcription factor HB34 suppresses jasmonic acid biosynthesis but promotes the expression of growth-related genes to balance plant immunity and growth in Arabidopsis.Plant Commun. 2025 Sep 8;6(9):101429. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2025.101429. Epub 2025 Jun 24. Plant Commun. 2025. PMID: 40566683
-
The Arabidopsis thaliana lectin receptor kinase LecRK-I.9 is required for full resistance to Pseudomonas syringae and affects jasmonate signalling.Mol Plant Pathol. 2017 Sep;18(7):937-948. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12457. Epub 2016 Sep 15. Mol Plant Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27399963 Free PMC article.
-
The plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Bacillus cereus AR156 induces systemic resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana by simultaneously activating salicylate- and jasmonate/ethylene-dependent signaling pathways.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2011 May;24(5):533-42. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-09-10-0213. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2011. PMID: 21198361
-
Defense-related callose deposition in plants against pathogens: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Aug;320(Pt 4):146005. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.146005. Epub 2025 Jul 13. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40664322 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
