Tumor cell-adipocyte gap junctions activate lipolysis and contribute to breast tumorigenesis
- PMID: 40835606
- PMCID: PMC12368202
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62486-3
Tumor cell-adipocyte gap junctions activate lipolysis and contribute to breast tumorigenesis
Abstract
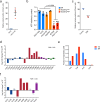
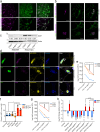
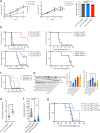
A pro-tumorigenic role for adipocytes has been identified in breast cancer, and reliance on fatty acid catabolism found in aggressive tumors. The molecular mechanisms by which tumor cells coopt neighboring adipocytes, however, remain incompletely understood. Here, we describe a direct interaction linking tumorigenesis to adjacent adipocytes. We examine breast tumors and their normal adjacent tissue from several patient cohorts, patient-derived xenografts, and mouse models, and find that lipolysis and lipolytic signaling are activated in neighboring adipose tissue. We find that functional gap junctions form between breast cancer cells and adipocytes. As a result, cAMP is transferred from breast cancer cells to adipocytes and activates lipolysis in a gap junction-dependent manner. We find that connexin 31 (GJB3) promotes receptor triple negative breast cancer growth and activation of lipolysis in vivo. Thus, direct tumor cell-adipocyte interaction contributes to tumorigenesis and may serve as a new therapeutic target in breast cancer.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA166945/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 CA243468/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB028148/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- W81XWH-12-1-0272/United States Department of Defense | United States Army | Army Medical Command | Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs (CDMRP)
- R01CA17447/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- F99 CA212488/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DK110426/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DK110426/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007334/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- W81XWH-21-1-0774/United States Department of Defense | United States Army | Army Medical Command | Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs (CDMRP)
- R01 CA257652/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 2R01EB028148/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

