Synchronous post-exercise electrocardiogram, phonocardiogram, photoplethysmograms and seismocardiogram
- PMID: 40835611
- PMCID: PMC12368122
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-025-05781-4
Synchronous post-exercise electrocardiogram, phonocardiogram, photoplethysmograms and seismocardiogram
Abstract
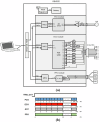
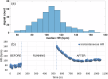
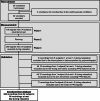
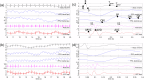
Noninvasive electromechanical assessment of cardiovascular function is emerging as a cost-effective method for diagnosis of heart failure and arterial diseases, and for telemedical monitoring of blood pressure and neural disorders. It encompasses simultaneous acquisition of electrocardiographic, phonocardiographic, arterial-pulse, chest-vibration, bioimpedance and other waveforms. The phases and amplitudes of these waveforms are used for construction of disease biomarkers. The procedure includes corrections of biomarker values to daily variation and excursions of heart rate. However, datasets that enable a systematic study of the effects of heart rate on mechanical waveforms are currently not available. Here, we describe SensSmartTech - the first dataset of multiparametric cardiovascular signals systematically measured in a large span of heart rates from 52 to 182 beats per minute, achieved by running on a treadmill. Besides providing the data for biomarker correction, the dataset enables new insights into the cardio-respiratory and electro-mechanical couplings in the cardiovascular system.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: V. A., J. P. and Lj. H. report the affiliation to the HeartBeam, Inc., but no competing interests regarding the reported research and the data.
Figures

References
-
- Tsao, C. W. et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics - 2022 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association 2022. Circulation145, e153–e639 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Turnbull, S. et al. Accuracy of a Single-Lead ECG Device for Diagnosis of Cardiac Arrhythmias Compared Against Cardiac Electrophysiology Study. Heart, Lung and Circulation33, 1465–1474 (2024). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

