Association between weight-adjusted waist index and severe periodontitis using NHANES 2009-2014
- PMID: 40835657
- PMCID: PMC12368046
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-14664-y
Association between weight-adjusted waist index and severe periodontitis using NHANES 2009-2014
Abstract
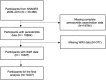
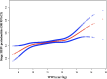
The Weight-adjusted Waist Index (WWI) is a novel anthropometric indicator for assessing obesity. Given the well-established association between obesity and periodontitis, this cross-sectional clinical study aimed to investigate the relationship between WWI and severe periodontitis while evaluating its potential as a simple predictive marker for periodontitis. The study analyzed periodontal examination data and WWI measurements from participants in the 2009-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), employing weighted logistic regression, smoothed curve fitting, and subgroup analyses. Among the 10,307 eligible participants, results demonstrated a significant positive correlation between WWI and the prevalence of stage III/IV periodontitis. After comprehensive adjustment for all confounding factors, each 1-unit increase in WWI was associated with a 1.19-fold higher risk of stage III/IV periodontitis (OR = 1.19, 95% CI 1.06-1.32, P = 0.007977). Subgroup analysis revealed that this association showed statistically significant variation only in the hypertension subgroup, indicating that the WWI-severe periodontitis relationship is particularly applicable to non-hypertensive individuals. These findings confirm that WWI can serve as a novel obesity-based predictive indicator for severe periodontitis.
Keywords: Cross-sectional study; NHANES; Obesity; Periodontitis; Weight-adjusted waist index.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Chen, M. X., Zhong, Y. J., Dong, Q. Q., Wong, H. M. & Wen, Y. F. Global, regional, and national burden of severe periodontitis, 1990–2019: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. J. Clin. Periodontol.48, 1165–1188. 10.1111/jcpe.13506 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- No. 1115B20500515/Postgraduate scientific research innovation promotion project of Hangzhou Normal University
- No. 20211231Y028/Guided Project of Science and Technology of Hangzhou
- No. 2024ZL724/Zhejiang Science and Technology Program of Chinese Medicine
- No. A20210056/Health and Science Project of Hangzhou
- No. 2021WJCY131/Hangzhou Biological Medicine and Health Industry Development Support Science and Technology Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

