Integrating network pharmacology and molecular modeling to decipher the anti-esophageal squamous cell carcinoma mechanisms of Bidens pilosa L
- PMID: 40836204
- PMCID: PMC12367626
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-03441-y
Integrating network pharmacology and molecular modeling to decipher the anti-esophageal squamous cell carcinoma mechanisms of Bidens pilosa L
Abstract
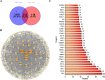
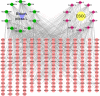
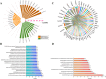
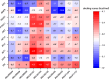
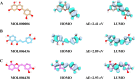
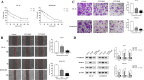
Bidens pilosa L (BL), known for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer properties across multiple malignancies, was investigated for its potential therapeutic effects against esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Through integrative network pharmacology and computational approaches, 10 bioactive compounds from BL were identified from HERB 2.0, symMap, BATMAN-TCM (target prediction score cutoff = 20, adjusted P-value = 0.05 for target analyses), TCMSP (oral bioavailability ≥ 30% and drug likeness ≥ 0.18), and ETCM 2.0 databases, while 3,993 ESCC-associated targets were retrieved from OMIM, GeneCards, and DisGeNET. Cross-analysis revealed 214 shared targets, with tyrosine-protein kinase, epidermal growth factor receptor, and alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase emerging as central hubs in protein-protein interaction networks. Functional enrichment analysis highlighted significant involvement in cellular responses to hormone stimuli, nitrogen compounds, and phosphorylation, with key pathways including cancer, PI3K-Akt, and Ras signaling. Molecular docking demonstrated high-affinity binding of (2E)-2-(3,4-Dihydroxybenzylidene)-6,7-Dihydroxy-Benzofuran-3-One (− 10.4 kcal/mol), Luteolin (− 10.1 kcal/mol), and Okanin (− 9.7 kcal/mol) to matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP9), specifically targeting catalytic residues GLU227 and TYR245. Quantum chemical calculations further revealed narrow HOMO-LUMO gaps for Luteolin (ΔE = 2.41 eV) and Okanin (ΔE = 2.93 eV), indicating high reactivity, while molecular dynamics simulations confirmed stable MMP9-ligand complexes (nearly − 200 kJ/mol), with Okanin exhibiting faster equilibration than Luteolin. The analysis of datasets from TCGA and GEO revealed that MMP9 is significantly upregulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissues compared to normal esophageal tissues. Meanwhile, Luteolin significantly inhibited the proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) capabilities of ESCC in vitro experiments.These findings collectively suggest that BL exerts anti-ESCC effects in silico through multi-target synergy, with Luteolin and Okanin identified as promising MMP9 inhibitors, providing a mechanistic foundation for future drug development.
Supplementary Information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s12672-025-03441-y.
Keywords: Bidens pilosa L; Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; Molecular docking; Molecular dynamics simulation; Molecular orbital calculations; Network pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Exploring the mechanism of action of Bidens pilosa L. in combating hepatic fibrosis through network pharmacology and molecular docking: An observational study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Sep 13;103(37):e39725. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039725. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39287276 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the Impact of Bidens pilosa on Behavioral, Oxidative Stress and Cerebellar Cortical Histoarchitectural Alterations During Bisphenol A Exposure in Mice.J Exp Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 27;17:403-416. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S522973. eCollection 2025. J Exp Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40606320 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the hub genes and mechanisms of Daphne altaica treating esophageal squamous cell carcinoma based on network pharmacology and bioinformatics analysis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Sep;149(11):8467-8481. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04797-w. Epub 2023 Apr 23. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37087696 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the phytochemical profile, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of Bidens pilosa: A Systematic Review.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Aug 1;16:1569527. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1569527. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40822453 Free PMC article.
-
Botanical, Pharmacological, Phytochemical, and Toxicological Aspects of the Antidiabetic Plant Bidens pilosa L.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:698617. doi: 10.1155/2014/698617. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014. PMID: 24616740 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73:17–48. - PubMed
-
- Colquhoun A, Arnold M, Ferlay J, Goodman KJ, Forman D, Soerjomataram I. Global patterns of cardia and non-cardia gastric cancer incidence in 2012. Gut. 2015;64:1881–8. - PubMed
-
- Morgan E, Soerjomataram I, Rumgay H, Coleman HG, Thrift AP, Vignat J, et al. The global landscape of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence and mortality in 2020 and projections to 2040: new estimates from GLOBOCAN 2020. Gastroenterology. 2022;163:649–e6582. - PubMed
-
- Gordaliza M. Natural products as leads to anticancer drugs. Clin Transl Oncol. 2007;9:767–76. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
