Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for treatment of diabetes and obesity: advantage of oral delivery
- PMID: 40836975
- PMCID: PMC12363265
- DOI: 10.3389/fddev.2024.1456654
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for treatment of diabetes and obesity: advantage of oral delivery
Abstract
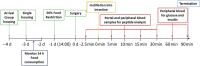
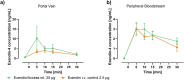
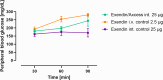
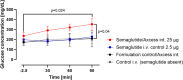
GLP-1 receptor agonists ((GLP-1 RAs) are currently receiving a lot of attention because of their impact in diabetes, weight loss and other areas. While GLP-1 RAs in injectable form are highly efficacious, further work is required to develop oral versions which can deliver these peptides efficiently without requiring use of excessively high doses. This paper describes the ability of an oral peptide delivery formulation, Axcess™, to enhance uptake of GLP-1 receptor agonists via the intestine, resulting in changes in insulin and glucose blood levels indicative of biopotencies of 9% for exendin-4 and 14.8% for semaglutide in preclinical models. The route of delivery suggests that the peptides will be able to interact with the GLP-1 receptors on the vagal afferents of the intestine, as is the case for native GLP-1 in healthy individuals. GLP-1 receptor agonists administered via this route will be a valuable addition to the therapeutic modalities available for treatment of diabetes and obesity.
Keywords: GLP-1; diabetes; obesity; oral delivery; peptide; vagal afferents.
Copyright © 2024 New, Bogus, Travers, Hahn, Vaiceliunaite, Burnet, Wang and Wen.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors RN, MBo, and GT were employed by Diabetology Ltd. Authors UH, AV, and MBu were employed by Synovo GmbH. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Gier B., Matveyenko A. V., Kirakossian D., Dawson D., Dry S. M., Butler P. C. (2012). Chronic GLP-1 receptor activation by Exendin-4 induces expansion of pancreatic duct glands in rats and accelerates formation of dysplastic lesions and chronic pancreatitis in the KrasG12D mouse model. Diabetes 16, 1250–1262. 10.2337/db11-1109 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

