Electrospun patches to deliver combination drug therapy for fungal infections
- PMID: 40836985
- PMCID: PMC12363251
- DOI: 10.3389/fddev.2024.1458009
Electrospun patches to deliver combination drug therapy for fungal infections
Abstract
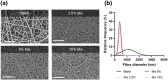
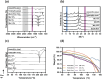
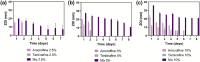
Fungal infections, though affecting healthcare globally, receive insufficient attention in clinical and academic settings. Invasive fungal infections, particularly caused by combat wounds, have been identified as a critical threat by the US Department of Defense. Monotherapy with traditional antifungals is often insufficient, and so combination therapies are explored to enhance treatment efficacy. However, systemic combination treatments can result in severe adverse effects, suggesting the need for localised delivery systems, such as drug-loaded electrospun patches, to administer antifungals directly to the infection site. This proof-of-concept study hypothesised that dual amorolfine and terbinafine therapy slowly releasing from electrospun patches would be an effective way of eradicating Candida albicans when the patch was applied directly to the fungal colony. The feasibility of creating electrospun materials loaded with amorolfine and terbinafine for combination antifungal therapy was investigated. Electrospinning was used to fabricate polycaprolactone (PCL) patches with varying drug loadings (2.5%, 5%, and 10% w/w) of amorolfine and terbinafine either individually or in combination. The incorporation of both drugs in the fibres was confirmed, with the drugs predominantly in an amorphous state. Results showed that combination therapy patches had a significantly greater and prolonged antifungal effect compared to monotherapy patches, with larger zones of inhibition and sustained efficacy over at least 7 days. This study therefore demonstrates that PCL-based electrospun patches containing amorolfine and terbinafine provide superior antifungal activity against C. albicans compared to monotherapy patches. This approach could lower required drug doses, reducing adverse effects, and enhance patient compliance due to prolonged drug release, leading to more effective antifungal therapy.
Keywords: drug combination; electrospinning; fungus; infection; patch.
Copyright © 2024 Dziemidowicz, Meszarik, Piovesan, Almatroudi, Williams and Murdan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- Abd-Elmonem E. M., Makky A. M. A., Antar A., Abd-Elsalam W. H., Khalil I. A. (2023). Corneal targeted amorolfine HCl-mixed micelles for the management of ocular candidiasis: preparation, in vitro characterization, ex vivo and in vivo assessments. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 85, 104614. 10.1016/j.jddst.2023.104614 - DOI
-
- Baran R., Sigurgeirsson B., Berker D. de, Kaufmann R., Lecha M., Faergemann J., et al. (2007). A multicentre, randomized, controlled study of the efficacy, safety and cost‐effectiveness of a combination therapy with amorolfine nail lacquer and oral terbinafine compared with oral terbinafine alone for the treatment of onychomycosis with matrix involvement. Br. J. Dermatology 157 (1), 149–157. 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.07974.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

