Comparative efficacy of eight traditional Chinese medicines combined with statins in the treatment of hyperlipidemia: a Bayesian network meta-analysis
- PMID: 40837400
- PMCID: PMC12361126
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1614767
Comparative efficacy of eight traditional Chinese medicines combined with statins in the treatment of hyperlipidemia: a Bayesian network meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Hyperlipidemia drives global cardiovascular mortality by elevating risks of atherosclerosis and stroke. While statins are foundational, traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) are widely combined with statins to boost efficacy. However, diverse TCM formulations lack comparative evidence in combination regimens, necessitating urgent evidence-based optimization.
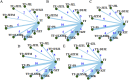
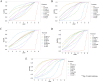
Methods: Based on preliminary literature review and component usage frequency analysis, 8 TCMs were included firstly. Then, we conducted a systematic search for RCTs that assessed 8 TCMs with traditional statin drugs (TT) for the treatment of hyperlipidemia. The search was conducted through September 30, 2024, and encompassed China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Chinese Biomedical Literature Database (CBM), Database of Chinese Sci-Tech Periodicals (VIP), Wanfang Database, PubMed, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library. Outcomes included clinical total effective rate, total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). Risk of bias in RCTs was evaluated using Cochrane's bias risk tool. Evidence synthesis was performed utilizing both direct and Bayesian network meta-analyses (NMA). Meta-regression analysis, subgroup analysis, publication bias analysis, and sensitivity analysis were employed to evaluate heterogeneity sources and efficacy robustness. Ranking analysis was implemented to comparatively assess clinical efficacy among eight TCMs. Evidence quality for each outcome was assessed using Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation approach (GRADE). Overall, the proposed structured framework integrated high-frequency TCM screening, NMA-driven efficacy ranking, methodological validation, and mechanistic investigation to holistically evaluate therapeutic interventions for the first time.
Results: 67 RCTs involving 7327 individuals and 8 TCMs were encompassed. Related analyses indicated TT + TCMs were more efficacious than TT monotherapy. Among 8 TCMs + TT, TT combined with Jiangzhi Tongmai Capsule (TT + JZTM) demonstrated the highest clinical total effective rate, TT combined with Dantian Jiangzhi Pill (TT + DTJZ) was the most effective in reducing TC, TT combined with Pushen Capsule (TT + PS) was the most effective in reducing TG, and TT combined with Jiangzhiling Tablet (TT + JZL) was the most effective in increasing HDL-C and reducing LDL-C.
Conclusion: NMA revealed the overall clinical efficacy of TT + JZL, TT + DTJZ, and TT + JZTM were ranked at the forefront in treating hyperlipidemia. These findings provide evidence-based guidance for tailoring TCM-statin combinations to target individualized lipid profiles.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42024603979, identifier [CRD42024603979].
Keywords: clinical efficacy; hyperlipidemia; network meta-analysis; safety outcome; traditional Chinese medicines.
Copyright © 2025 Jiang, Fan, Zhou, Liu, Pan, Yang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of 11 oral preparations of single-source traditional Chinese medicines in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 24;16:1582661. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1582661. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40630122 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for central serous chorioretinopathy: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jun 16;6(6):CD011841. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011841.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40522203
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Cieza A., Causey K., Kamenov K., Hanson S. W., Chatterji S., Vos T. (2021). Global estimates of the need for rehabilitation based on the global burden of disease study 2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet 396 (10267), 2006–2017. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32340-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

