Poor-tasting pediatric medicines: Part 1. A scoping review of their impact on patient acceptability, medication adherence, and treatment outcomes
- PMID: 40837710
- PMCID: PMC12360445
- DOI: 10.3389/fddev.2025.1553286
Poor-tasting pediatric medicines: Part 1. A scoping review of their impact on patient acceptability, medication adherence, and treatment outcomes
Abstract
Background: Many medicines for children taste bitter and unpleasant, presenting a significant barrier to effective pharmacotherapy. Anecdotally, this issue is widely recognized; however, empirical evidence on the consequences of unpalatable medicines remains scarce and fragmented. The objective of this scoping review was to investigate the impact of poor tasting pediatric medicines on patient acceptability, medication adherence, and/or treatment outcomes.
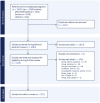
Methods: A literature search was performed in MEDLINE/PubMed, EMBASE and CINAHL from inception to June 2023. Eligibility criteria included interventional or observational studies conducted in children aged 0-18 years (population), administered an unpalatable oral medicine (exposure), with any reported impact on patient acceptability, medication adherence, and treatment effects (outcomes). Study screening and data extraction was completed using a standardized form on Covidence.
Results: After searching 2,282 citations and reviewing 429 full-text papers, 225 articles were included in the final analysis. The impact of poor-tasting medicines was observed across 77 diseases or indications, with 156 different unpalatable medicinal products identified. Outcomes were most frequently linked to reduced patient acceptability, with 64% of articles reporting rejection responses, the need for strategies to aid administration (from positive reinforcement to physical restraint and forced administration), and impacts on prescribing practices (e.g., use of non-first line alternative therapies). Medication adherence impacts were reported in 27% of the reviewed studies, where poor taste was reported as a barrier to adherence in chronic diseases and correlated with incomplete dose administration in acute conditions. A small number of studies linked palatability with treatment outcomes, including viral suppression in HIV and seizure control in epilepsy.
Conclusion: This review highlights the widespread adverse impact of poor-tasting pediatric medicines on patient experiences and outcomes, though the true extent of the issue may still be underreported. The problem affects children worldwide, across all age groups, and is frequently noted by parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals in both clinical and domiciliary settings. These findings emphasize the need for the development and prescription of more palatable medicines for children, as well as the advancement of more universal taste-masking strategies to address this widespread problem.
Keywords: acceptability; adherence; bitter; children; medicines; outcomes; palatability; taste.
Copyright © 2025 Ranmal, Walsh and Tuleu.
Conflict of interest statement
Author SRR was employed by Sciense Ltd. Author JW was employed by Jenny Walsh Consulting Ltd. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Abdulla S., Amuri B., Kabanywanyi A. M., Ubben D., Reynolds C., Pascoe S., et al. (2010). Early clinical development of artemether-lumefantrine dispersible tablet: palatability of three flavours and bioavailability in healthy subjects. Malar. J. 9 (1), 253. 10.1186/1475-2875-9-253 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abu-Khalaf N., Zaid A. N., Jaradat N., AlKilany A., Abu Rumaila B., Al Ramahi R., et al. (2018). The taste of commercially available clarithromycin oral pharmaceutical suspensions in the Palestinian market: electronic tongue and in vivo evaluation. Sensors (Basel) 18 (2), 454. 10.3390/s18020454 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

