Advanced drug delivery systems for oral squamous cell carcinoma: a comprehensive review of nanotechnology-based and other innovative approaches
- PMID: 40837711
- PMCID: PMC12360444
- DOI: 10.3389/fddev.2025.1596964
Advanced drug delivery systems for oral squamous cell carcinoma: a comprehensive review of nanotechnology-based and other innovative approaches
Abstract
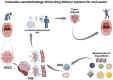
Oral cancer, particularly oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), poses significant challenges due to its aggressiveness, high metastatic potential, and resistance to conventional therapies. Recent advancements in drug delivery systems (DDS), including nanotechnology, intelligent hydrogels, lipid nanoparticles, and photodynamic therapy (PDT), offer innovative solutions for targeted treatment. These DDS utilize tumor-specific stimuli, such as pH variations, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and enzymatic activity, to achieve precise drug release while minimizing systemic toxicity. Cutting-edge technologies, such as microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and artificial intelligence (AI), are enhancing the precision and personalization of DDS. Combination therapies integrating chemotherapy, PDT, and immunotherapy show promise in overcoming current limitations. Despite significant progress, challenges remain in scalability, patient-specific customization, and safety assessments. This review synthesizes the state-of-the-art in DDS for OSCC, highlighting future directions and the need for interdisciplinary collaboration to improve therapeutic outcomes and patient quality of life.
Keywords: drug delivery systems; immunotherapy; intelligent hydrogels; lipid nanoparticles; nanotechnology; oral cancer; oral squamous cell carcinoma; photodynamic therapy.
Copyright © 2025 Herrada Céspedes, Reyes and Morales.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hydrogel-driven innovations for targeted delivery, immune modulation, and tissue repair in thyroid cancer therapy.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jul 25;13:1608709. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1608709. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40791984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Innovative approaches for cancer treatment: graphene quantum dots for photodynamic and photothermal therapies.J Mater Chem B. 2024 May 8;12(18):4307-4334. doi: 10.1039/d4tb00255e. J Mater Chem B. 2024. PMID: 38595268 Review.
-
Novel receptor tyrosine kinase-targeted strategies to overcome resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Pharmacol Rep. 2025 Aug;77(4):962-982. doi: 10.1007/s43440-025-00745-2. Epub 2025 Jun 5. Pharmacol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40468099 Review.
-
Emerging innovations in ophthalmic drug delivery for diabetic retinopathy: a translational perspective.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Jul 20. doi: 10.1007/s13346-025-01925-6. Online ahead of print. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40685494
References
-
- Agarwal S., Yadav A. S., Dinesh V., Vatsav K. S. S., Prakash K. S. S., Jaiswal S. (2023). By artificial intelligence algorithms and machine learning models to diagnosis cancer. Mater. Today Proc. 80, 2969–2975. 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.07.088 - DOI
-
- Ahmad A., Ansari M. M., AlAsmari A. F., Ali N., Maqbool M. T., Raza S. S., et al. (2021). Dose dependent safety implications and acute intravenous toxicity of aminocellulose-grafted-polycaprolactone coated gelatin nanoparticles in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 192, 1150–1159. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.028 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

