Toward Home-Based Telerehabilitation for Cerebral Palsy Patients: A Qualitative Study on Feasibility, Barriers and Facilitators
- PMID: 40837718
- PMCID: PMC12361637
- DOI: 10.1002/hsr2.71131
Toward Home-Based Telerehabilitation for Cerebral Palsy Patients: A Qualitative Study on Feasibility, Barriers and Facilitators
Abstract
Background and aim: Telerehabilitation has emerged as a promising solution to address accessibility, cost-effectiveness, and continuity of care for patients requiring long-term rehabilitation, like cerebral palsy (CP) patients. This study aimed to qualitatively explore the perceptions of clinical specialists, and CP patients regarding the feasibility, barriers, and facilitators of home-based telerehabilitation.
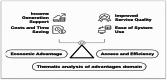
Methods: This qualitative study conducted a thematic analysis approach. Participants include two groups: 17 medical informatics and rehabilitation professionals and 13 CP patients and/or their caregivers. Participants were selected via expert and snowball sampling. Interviews were semi-structured, transcribed, and analyzed using the Braun-Clarke thematic analysis technique and MAXQDA software.
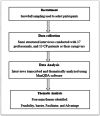
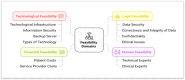
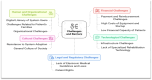
Results: Thematic analysis revealed four dominant themes including feasibility, barriers, facilitators, and advantages. Feasibility was affected by technological infrastructure (internet connectivity, data security), human resources (availability of multidisciplinary specialists), legal aspects (patient data privacy), and financial sustainability. Key barriers included low digital literacy, limited access to specialized rehabilitation technologies, cultural resistance, legal regulations, and financial constraints. The findings also highlighted several advantages of home-based telerehabilitation, including cost savings, improved accessibility to rehabilitation, and enhanced patient engagement in therapy.
Conclusion: The current study suggested that home-based telerehabilitation can be a feasible alternative for CP patients in Iran, but a variety of technological, financial, legal, and cultural barriers must first be addressed for its successful development. Overcoming such barriers requires targeted investments, supportive policies, and cultural education for successful implementation.
Keywords: Health Information Technology; cerebral palsy; home‐Based Care; qualitative research; rehabilitation services; telerehabilitation.
© The Author(s). Health Science Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript. Dr. [Alireza Rahimi] had full access to all of the data in this study and takes complete responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Barriers and facilitators to the implementation of lay health worker programmes to improve access to maternal and child health: qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Oct 8;2013(10):CD010414. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010414.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24101553 Free PMC article.
-
Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314
-
Factors that influence caregivers' and adolescents' views and practices regarding human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination for adolescents: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Apr 15;4(4):CD013430. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013430.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40232221 Free PMC article.
-
An AI-Based Telerehabilitation Solution to Improve Mobility in People With Multiple Sclerosis (the PLATINUMS Project): Protocol for an Implementation and Evaluation Study.JMIR Res Protoc. 2025 Jul 24;14:e75983. doi: 10.2196/75983. JMIR Res Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40705418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharmin S., Faith B., Prieto Martín P., and Ramalingam B., The Contribution of Digital Technologies to Service Delivery: An Evidence Review. (2017).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

