Enhancing wheat genomic prediction by a hybrid kernel approach
- PMID: 40838078
- PMCID: PMC12363290
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1605202
Enhancing wheat genomic prediction by a hybrid kernel approach
Abstract
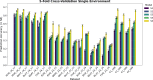
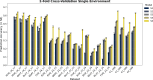
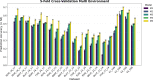
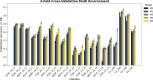
This study integrates genomic and pedigree data by leveraging advanced modeling techniques, aiming to enhance the predictive performance of genomic selection models by capturing complex genetic relationships through the interaction of both matrices and exploring the utility of non-linear methods, such as kernel matrices. Our goal was to improve genomic prediction accuracy by combining the pedigree-based or genetic similarity matrix ( A ) with the genomic similarity matrix ( G ). Using various wheat datasets, we performed five single-environment models and five multi-environment models that incorporated genotype-by-environment (G × E) interactions. The proposed models S5 and M5 significantly enhanced prediction accuracy by incorporating two novel symmetric kernels, C and P , derived from the interaction of genomic and pedigree matrices. These hybrid kernels captured additional, independent genetic variation not explained by conventional matrices. The proposed prediction model outperformed the standard conventional models in most single-environment and multi-environment models. The genomic models with non-linear kernels were better predictors than the linear prediction models.
Keywords: genomics; genotype by environment interaction; merging genomics and pedigree; pedigree; single-environment.
Copyright © 2025 Cuevas, Crossa, Montesinos-López, Martini, Gerard, Ortegón, Dreisigacker, Govindan, Pérez-Rodríguez, Saint Pierre, Herrera, Montesinos-López and Vitale.
Conflict of interest statement
Author JM was employed by the company Aardevo B.V. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Multi-task genomic prediction using gated residual variable selection neural networks.BMC Bioinformatics. 2025 Jul 7;26(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s12859-025-06188-z. BMC Bioinformatics. 2025. PMID: 40624470 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance perfusion for differentiating low-grade from high-grade gliomas at first presentation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 22;1(1):CD011551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29357120 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

