DNMT1-mediated SPINT2 expression drives early senescence by suppressing c-Met signaling in human fibroblasts
- PMID: 40838961
- PMCID: PMC12422819
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.206303
DNMT1-mediated SPINT2 expression drives early senescence by suppressing c-Met signaling in human fibroblasts
Abstract
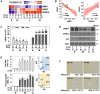
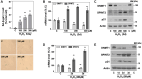
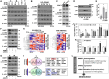
Cellular senescence is a critical process involved in aging and related disorders, yet the molecular triggers of early senescence remain elusive. Here, we identify DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) downregulation as a key trigger of early senescence and establish serine protease inhibitor Kunitz type 2 (SPINT2) as its critical downstream effector. Using replicative and oxidative stress-induced senescence models of primary human diploid fibroblast, we observed persistent upregulation of SPINT2 and inverse downregulation of DNMT1, preceding senescence-associated β-galactosidase activity, a conventional senescence marker. Pharmacological inhibition and siRNA-mediated knockdown of DNMT1 significantly increased SPINT2 expression and induced senescence, showing mitigated effects by SPINT2 knockdown. Furthermore, SPINT2 overexpression alone induced senescence. Methylation-specific sequencing identified four CpG sites in SPINT2 promoter, that became hypomethylated at early transition of senescence and upon DNMT1 suppression. Functional analyses revealed that DNMT1-mediated SPINT2 expression induced c-Met inhibition, triggering senescence. Transcriptomic profiling identified 17 commonly deregulated c-Met signaling genes in both senescence models, with COL27A1, STAM2, and CBL validated as key downstream targets of SPINT2/c-Met signaling. These findings establish DNMT1-mediated SPINT2 upregulation as a novel epigenetic mechanism driving senescence initiation via c-Met inhibition, providing insights into the early stage of senescence and potential therapeutic targets for aging-related diseases.
Keywords: DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1); aging; cellular senescence; senescence; serine protease inhibitor Kunitz type 2 (SPINT2).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

