Investigating the role of FOX gene family in development and stress response in Labeo rohita: A multi-faceted analysis of phylogeny and genome characterization
- PMID: 40839711
- PMCID: PMC12370200
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323740
Investigating the role of FOX gene family in development and stress response in Labeo rohita: A multi-faceted analysis of phylogeny and genome characterization
Abstract
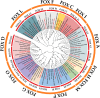
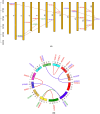
The forkhead box (FOX) gene family of transcription factors regulates muscle development, immune responses, and metabolic processes across species. Despite extensive studies on FOX genes in other organisms, their evolutionary and functional roles in Labeo rohita, an economically and ecologically important freshwater fish, remain unclear. Owing to its unique physiological and ecological traits, L. rohita is an ideal model for exploring these roles. Here, we present the first computational analysis of the FOX gene family in L. rohita, identifying 21 FOX genes. Physicochemical analysis revealed that most FOX proteins have a basic nature except for FOX A3, D3, I2, O1, O3, O4, P1, and P2. Instability index analysis indicated that all FOX proteins are unstable (values > 40), while hydrophobicity assessment showed that except FOX O1, all proteins are hydrophobic. Phylogenetic analysis grouped FOX homologs into 11 major clades with other vertebrates. All proteins exhibited structural homogeneity by sharing the Forkhead Box domain. Gene structure comparisons revealed seven duplicated pairs, and Circos analysis demonstrated organization into 20 clusters. This study highlights the critical roles of FOX genes and fills a significant knowledge gap, providing a foundation for future functional and phylogenomic studies with implications for aquaculture and evolutionary biology.
Copyright: © 2025 Naz et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Genome-wide characterization of GRAS gene family and their expression profiles under diverse biotic and abiotic stresses in Amorphophallus konjac.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jul 8;26(1):643. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11777-6. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40629278 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of POD gene family and expression differentiation under NaCl, H2O2 and PEG stresses in sorghum.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jul 17;26(1):674. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11858-6. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40676507 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Pascual-Carreras E, Herrera-Úbeda C, Rosselló M, Coronel-Córdoba P, Garcia-Fernàndez J, Saló E, et al. Analysis of Fox genes in Schmidtea mediterranea reveals new families and a conserved role of Smed-foxO in controlling cell death. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):2947. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80627-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

