Effectiveness of EPID-based in-vivo dosimetry with EPIgray® Software for head and neck VMAT treatments
- PMID: 40840947
- PMCID: PMC12392402
- DOI: 10.15537/smj.2025.46.8.20240844
Effectiveness of EPID-based in-vivo dosimetry with EPIgray® Software for head and neck VMAT treatments
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the effectiveness of in-vivo dosimetry (IVD) utilizing an electronic portal imaging device (EPID) in conjunction with EPIgray® software (DOSIsoft, Cachan, France) for assessing the accuracy of dose delivery for the patient when undertaking head and neck (H&N) treatments.
Methods: Using cross-sectional analysis, data were collected from the linear accelerator of twenty patients undergoing (H&N) radiotherapy treatments using the Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) modality from June 2019 to October 2023 at Gleneagles Hospital Penang, Penang, Malaysia. EPIgray® software reconstructed the delivered dose based on EPID images. These reconstructed doses were compared with the planned doses to evaluate dose accuracy, specifically looking at how many patient doses fell within the set tolerance range. In addition, RTsafe PseudoPatient™ phantom was involved in this study, and the reconstructed dose with EPIgray® was compared with the delivered dose and was established as a benchmark for accuracy.
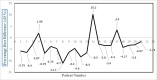
Results: The percentage difference between the reconstructed doses and planned doses (ΔD%) for patients ranged from (1.96) to (-11.1), and the results showed that 60% of the patients' doses were within the tolerance range (±5%). The phantom study resulted in a percentage dose difference (ΔD%) of -1.73%, and this was established as a benchmark for accuracy.
Conclusion: The study proves that using EPID-based in-vivo dosimetry with EPIgray® software is a precise way to check that the right amount of radiation is being delivered for patients during radiotherapy to head and neck (H&N) treatments. Integrating EPIgray® into clinical practice enhances dose accuracy and patient safety.
Keywords: EPIgray®; PseudoPatient™ phantom; Radiotherapy; Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT).
Copyright: © Saudi Medical Journal.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evaluation of a Monte Carlo based EPID system for patient-specific IMRT and VMAT quality assurance.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025 Jul;26(7):e70178. doi: 10.1002/acm2.70178. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40660876 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric accuracy of low dose rate volumetric modulated arc therapy delivery in an Elekta Versa HD linear accelerator for pulsed low dose rate treatment of recurrent high-grade glioma using Monaco planning system: Low dose rate VMAT-based PLDR in Elekta Linac.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025 Sep;26(9):e70253. doi: 10.1002/acm2.70253. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40903817 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of an EPID-based dose verification system for patient-specific quality assurance in a harmony device.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025 Sep;26(9):e70201. doi: 10.1002/acm2.70201. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40841322 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of the precision and accuracy of dose measurements in photon radiotherapy using polymer and Fricke MRI gel dosimetry.Phys Med Biol. 2002 Oct 21;47(20):R107-21. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/47/20/201. Phys Med Biol. 2002. PMID: 12433119
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- IAEA. Development of procedures for in vivo dosimetry in radiotherapy. Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, IAEA; 2013.
-
- Petoukhova A, Snijder R, Vissers T, Ceha H, Struikmans H.. In vivo dosimetry in cancer patients undergoing intraoperative radiation therapy. Phys Med Biol 2023; 68: 18TR01. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

