Comparative analysis of S100A10 and S100A11 in MASLD and hepatic cancer development revealed a tumor suppressive role for S100A10
- PMID: 40841353
- PMCID: PMC12370981
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-025-07940-2
Comparative analysis of S100A10 and S100A11 in MASLD and hepatic cancer development revealed a tumor suppressive role for S100A10
Abstract
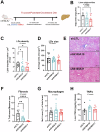
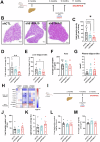
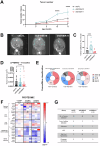
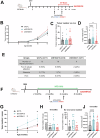
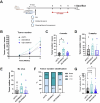
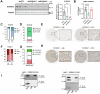
S100 proteins are significantly deregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). Here, we investigated the impact of hepatocyte downregulation of two closely-related members of the S100 family, S100A10 and S100A11, in complementary mouse models of MASLD and liver cancer. Hepatotropic AAV8 encoding shRNAs targeting S100A10 or S100A11 were used to downregulate these proteins specifically in the liver of mice fed a diet inducing hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis and in a genetic mouse model of MASLD bearing hepatocyte-specific deletion of PTEN (LPTENKO). The impact of S100A10 or S100A11 downregulation on liver tumor development was further investigated in aged LPTENKO mice spontaneously developing MASLD-driven HCC and in diethylnitrosamine (DEN)-injected mice fed or not with high fat diet. Finally, the upregulation and downregulations of S100A10 were performed in mice harbouring the over-expression of Myc and constitutively activated β-catenin, two main events occurring in a sub-type of human HCC. Downregulation of S100A10 promoted hepatocarcinogenesis in a fatty liver setting, while reducing steatosis and fibrosis development. S100A11 knock-down consistently reduced MASLD and tumoral growth. However, in vivo S100A11 downregulation triggered concomitant partial loss of endogenous protective S100A10. Overexpression of S100A10 reduced the volume of tumors and might represent a therapeutic option. The results show that both S100A10 and S100A11 play active roles in the development of MASLD. However, these two closely associated proteins present opposite contributions to hepatic cancer, S100A10 being protective and S100A11 deleterious.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Geneva Health Head Office (authorization number GE78) and was in accordance with the Swiss guidelines for animal experimentation.
Figures
References
-
- EASL-EASD-EASO. Clinical practice guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J Hepatol. 2024;81:492–542. - PubMed
-
- Younossi ZM. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease - A global public health perspective. J Hepatol. 2019;70:531–44. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 320030_200530/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
- 320030_200530/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
- 320030_200530/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
- 320030_200530/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
- 320030_200530/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
- 320030_200530/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
- 320030_200530/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
- 320030_200530/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
- 320030_200530/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
- 320030_200530/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
- 320030_200530/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
- 320030_200530/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

