DHX8 regulates degradation of RNA by RNautophagy
- PMID: 40842239
- PMCID: PMC12370622
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf801
DHX8 regulates degradation of RNA by RNautophagy
Abstract
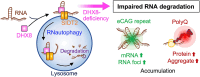
RNautophagy is an intracellular degradation pathway in which RNA is directly taken up by lysosomes. The cytoplasmic regions of the lysosomal membrane proteins, LAMP2C and SIDT2, can interact with consecutive guanine sequences in RNA, mediating the uptake of RNA during RNautophagy. RNautophagy has also been implicated in the clearance of expanded CAG-repeat mRNA and RNA foci associated with polyQ disease. However, the mechanisms of RNA uptake during RNautophagy remain unclear. Here, we screened for proteins that bind consecutive guanine sequences and identified RNA helicase DHX8 as a binding partner. DHX8 interacts with SIDT2 and is partially localized to the cytoplasmic side of the lysosomal membrane. We found that DHX8 regulates intracellular RNA degradation via SIDT2-dependent RNautophagy but not via macroautophagy. RNA binding, but not ATPase activity, of DHX8 is likely to be important for regulating RNA degradation. DHX8 also contributes to the clearance of pathogenic CAG repeat mRNA and RNA foci, and the levels of both soluble protein and insoluble high-molecular-weight aggregates of expanded polyQ tracts. Our findings provide insights into the mechanisms underlying the regulation of intracellular RNA degradation, autophagic pathways, and possibly the pathogenesis of repeat RNA-related disorders.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

