Recent advances in injectable hydrogels for osteoarthritis treatments
- PMID: 40843442
- PMCID: PMC12364895
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1644222
Recent advances in injectable hydrogels for osteoarthritis treatments
Abstract
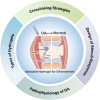
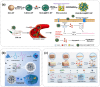
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease characterized by cartilage degradation, synovial inflammation, and subchondral bone alterations, poses significant challenges due to its high prevalence and associated disability. Injectable hydrogels have emerged as promising candidates for OA treatment due to their ability to deliver bioactive molecules directly to the affected joint, enhancing local efficacy while minimizing systemic side effects. This review focuses on recent advances in injectable hydrogels for OA treatment, emphasizing their structural design, functional properties, and therapeutic applications. We further discuss the advantages and limitations of natural, synthetic, and composite hydrogels, as well as innovative cross-linking strategies and stimuli-responsive behaviors. Thermosensitive, pH-responsive, enzyme-responsive, and multi-responsive hydrogels are highlighted for their potential to achieve intelligent drug delivery, inhibit cartilage degradation, and reduce inflammation. Overall, injectable hydrogels hold great promise for OA treatment and become an effective therapeutic option with further research and innovation.
Keywords: biocompatibility; injectable hydrogels; osteoarthritis; stimuli-responsive hydrogels; therapeutic hydrogels.
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Deng, Wang, Liu, Hu, Luan, Zhu and Zheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Bandyopadhyay A., Ghibhela B., Shome S., Pal D., Nandi S. K., Mandal B. B. (2024). Silk-based injectable photocurable hydrogel loaded with autologous growth factors for patient-specific repair of meniscal defects in vivo . Appl. Mater. Today 37, 102111. 10.1016/j.apmt.2024.102111 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

