The Novel Achievements in Oncological Metabolic Radio-Therapy: Isotope Technologies, Targeted Theranostics, Translational Oncology Research
- PMID: 40843729
- PMCID: PMC12372036
- DOI: 10.3390/medsci13030107
The Novel Achievements in Oncological Metabolic Radio-Therapy: Isotope Technologies, Targeted Theranostics, Translational Oncology Research
Abstract
Background/objectives: This manuscript presents an overview of advances in oncological radiotherapy as an effective treatment method for cancerous tumors, focusing on mechanisms of action within metabolite-antimetabolite systems. The urgency of this topic is underscored by the fact that cancer remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide: as of 2022, approximately 20 million new cases were diagnosed globally, accounting for about 0.25% of the total population. Given prognostic models predicting a steady increase in cancer incidence to 35 million cases by 2050, there is an urgent need for the latest developments in physics, chemistry, molecular biology, pharmacy, and strict adherence to oncological vigilance. The purpose of this work is to demonstrate the relationship between the nature and mechanisms of past diagnostic and therapeutic oncology approaches, their current improvements, and future prospects. Particular emphasis is placed on isotope technologies in the production of therapeutic nuclides, focusing on the mechanisms of formation of simple and complex theranostic compounds and their classification according to target specificity.
Methods: The methodology involved searching, selecting, and analyzing information from PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases, as well as from available official online sources over the past 20 years. The search was structured around the structure-mechanism-effect relationship of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The manuscript, including graphic materials, was prepared using a narrative synthesis method.
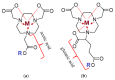
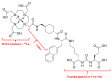
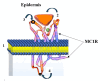
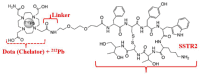
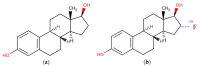
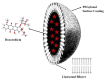
Results: The results present a sequential analysis of materials related to isotope technology, particularly nucleus stability and instability. An explanation of theranostic principles enabled a detailed description of the action mechanisms of radiopharmaceuticals on various receptors within the metabolite-antimetabolite system using specific drug models. Attention is also given to radioactive nanotheranostics, exemplified by the mechanisms of action of radioactive nanoparticles such as Tc-99m, AuNPs, wwAgNPs, FeNPs, and others.
Conclusions: Radiotheranostics, which combines the diagnostic properties of unstable nuclei with therapeutic effects, serves as an effective adjunctive and/or independent method for treating cancer patients. Despite the emergence of resistance to both chemotherapy and radiotherapy, existing nuclide resources provide protection against subsequent tumor metastasis. However, given the unfavorable cancer incidence prognosis over the next 25 years, the development of "preventive" drugs is recommended. Progress in this area will be facilitated by modern medical knowledge and a deeper understanding of ligand-receptor interactions to trigger apoptosis in rapidly proliferating cells.
Keywords: cancer epidemiology; mABs-drug; peptide receptor radionuclide therapy; radiotherapy; target complexes; targeted nuclides; theranostics; translational oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



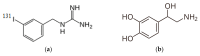



References
-
- Abergel R., Aris J., Bolch W.E., Dewji S.A., Golden A., Hooper D.A., Margot D., Menker C.G., Paunesku T., Schaue D., et al. The enduring legacy of Marie Curie: Impacts of radium in 21st century radiological and medical sciences. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2022;98:267–275. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2022.2027542. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

