A reduction in serum IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-6, and GM-CSF serves as potential markers for a positive outcome to lumbar epidural steroid injections
- PMID: 40844981
- PMCID: PMC12373237
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0329552
A reduction in serum IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-6, and GM-CSF serves as potential markers for a positive outcome to lumbar epidural steroid injections
Abstract
Introduction: This study evaluated serum inflammatory cytokine levels before and after transforaminal epidural steroid injections (TFESI) to assess their potential as biomarkers for predicting favorable outcomes in patients with lumbosacral radiculopathy.
Methods: All 120 eligible patients diagnosed with lumbosacral radiculopathy underwent blood collection 1) before TFESI and 2) two weeks after the procedure. A 5.0 mg dexamethasone mixture with local anesthetics was injected at each epidural level. This study defined a favorable response as a pain reduction of more than 50% at the 2-week follow-up. Serum inflammatory cytokines between good and poor responders were analyzed. Data collection included pain characteristics, clinical presentations, and radiographic findings.
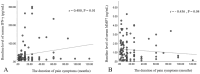
Results: Positive responses were observed in 73 out of 120 patients (60.8%). Patients with favorable responses demonstrated a significant reduction in serum IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-6, and GM-CSF concentration at 2 weeks after TFESI compared to their baseline levels. However, mean differences in serum inflammatory cytokines post-TFESI showed no significant variation between two groups. The duration of pain symptoms was associated with increased levels of IFN-γ and decreased levels of MMP7. The increased serum IL-6, GDF-15, and GM-CSF exhibited a significant correlation with clinical presentations. The higher level of serum IFN-γ significantly correlated with the severity of HNP (r = 0.436, P = 0.039) while the elevated serum concentration of MMP7 exhibited a significant correlation with the presence of foraminal stenosis (r = 0.436, P = 0.045).
Conclusion: The decrease in serum IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-6, and GM-CSF levels post-TFESI was a promising biomarker for a favorable response in patients with lumbosacral radiculopathy.
Copyright: © 2025 Chalermkitpanit et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

