Light-triggered molecular mechanotherapy of tumor using membrane-mimicking conjugated oligoelectrolytes
- PMID: 40845106
- PMCID: PMC12372874
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ady3349
Light-triggered molecular mechanotherapy of tumor using membrane-mimicking conjugated oligoelectrolytes
Abstract
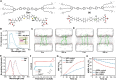
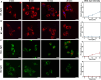
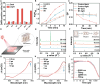
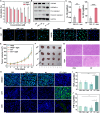
A class of light-mediated mechanotherapeutic agents was developed on the basis of conjugated oligoelectrolytes (COEs), which mimic the topology of lipid membranes and intrinsically exhibit excellent biocompatibility. Low-dose white light irradiation (20 milliwatts per square centimeter for 10 minutes) substantially decreased the half-maximal inhibitory concentration of the optimized COE against A549 cancer cells from more than 256 to 0.6 micromolar. Typical photodynamic and photothermal effects were not responsible for the potent anticancer efficacy. Biophysical and photophysical experiments using vesicle models revealed that COEs can induce mechanical force likely by molecular conformation change within lipid membranes under light exposure, supporting the mechanotherapeutic mechanism by which COEs after excitation can physically disrupt cell membrane. Investigation of two other COEs with similar spectral properties but different backbone architectures revealed that their mechanotherapeutic efficacy is dependent on molecular topology. These results highlight the potential to develop light-responsive mechanotherapeutic agents based on membrane-mimicking COE platform for cancer treatment.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Membrane Intercalation of a Conjugated Oligoelectrolyte Photosensitizer Enables Efficient Anticancer Photodynamic Therapy.Adv Healthc Mater. 2025 Jul;14(18):e2501300. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202501300. Epub 2025 May 24. Adv Healthc Mater. 2025. PMID: 40411856
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Nanoscale Curvature-Facilitated Membrane Intercalation of Conjugated Oligoelectrolytes Revealed by Nanobar-Supported Lipid Bilayers.ACS Nano. 2025 Aug 27. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5c05260. Online ahead of print. ACS Nano. 2025. PMID: 40864901
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
References
-
- Willyard C., Cancer therapy: An evolved approach. Nature 532, 166–168 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Siegel R. L., Giaquinto A. N., Jemal A., Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 74, 12–49 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Li J., Zhu L., Kwok H. F., Nanotechnology-based approaches overcome lung cancer drug resistance through diagnosis and treatment. Drug Resist. Updat. 66, 100904 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Zhao Y., Zhang L., Jiang T., Long J., Ma Z., Lu A., Cheng Y., Cao D., The ups and downs of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitors in cancer therapy–Current progress and future direction. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 203, 112570 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Zheng X., Song X., Zhu G., Pan D., Li H., Hu J., Xiao K., Gong Q., Gu Z., Luo K., Li W., Nanomedicine combats drug resistance in lung cancer. Adv. Mater. 36, 2308977 (2024). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

