Distinctive molecular features of radiation-induced thyroid cancers
- PMID: 40845117
- PMCID: PMC12372901
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adw7680
Distinctive molecular features of radiation-induced thyroid cancers
Abstract
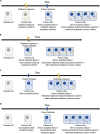
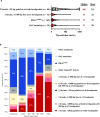
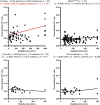
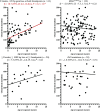
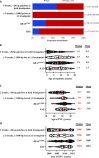
Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) incidence increased after childhood exposure to radioactive fallout from the Chornobyl accident. We investigated PTC genomic profiles to distinguish radiation-induced versus sporadic oncogenic drivers by modeling dose and molecular characteristics by driver category: BRAFV600E (n = 132), RAS mutation (n = 31), fusions generated from two breakpoints and <20 base pairs (bp) breakpoint gain/loss (Fusion2B<20bp; n = 63), or ≥3 breakpoints and ≥1000 bp breakpoint loss (n = 20). The frequency of Fusion2B<20bp-PTC increased with increasing thyroid radiation dose, whereas all others declined. Clonal small deletion counts increased with increasing radiation dose for Fusion2B<20bp-PTC (P = 5.1 × 10-4) but not other drivers (P > 0.08). Clonal clock mutational signatures, marking the age of tumor initiation, were associated with age at the accident for Fusion2B<20bp-PTC (P = 8.2 × 10-4) but not other drivers (P > 0.21). Together, these results support a causal role for ionizing radiation in Fusion2B<20bp-PTC as a group but not other drivers.
Figures
References
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. (Lyon, France, 2012).
-
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR), "Effects of Ionizing Radiation: United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation: UNSCEAR 2006 Report, Volume 1—Report to the General Assembly, with Scientific Annexes A and B" (United Nations Publication, 2008).
-
- Youk J., Kwon H. W., Lim J., Kim E., Kim T., Kim R., Park S., Yi K., Nam C. H., Jeon S., An Y., Choi J., Na H., Lee E. S., Cho Y., Min D. W., Kim H., Kang Y. R., Choi S. H., Bae M. J., Lee C. G., Kim J. G., Kim Y. S., Yu T., Lee W. C., Shin J. Y., Lee D. S., Kim T. Y., Ku T., Kim S. Y., Lee J. H., Koo B. K., Lee H., Yi O. V., Han E. C., Chang J. H., Kim K. S., Son T. G., Ju Y. S., Quantitative and qualitative mutational impact of ionizing radiation on normal cells. Cell Genom. 4, 100499 (2024). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Morton L. M., Karyadi D. M., Stewart C., Bogdanova T. I., Dawson E. T., Steinberg M. K., Dai J., Hartley S. W., Schonfeld S. J., Sampson J. N., Maruvka Y. E., Kapoor V., Ramsden D. A., Carvajal-Garcia J., Perou C. M., Parker J. S., Krznaric M., Yeager M., Boland J. F., Hutchinson A., Hicks B. D., Dagnall C. L., Gastier-Foster J. M., Bowen J., Lee O., Machiela M. J., Cahoon E. K., Brenner A. V., Mabuchi K., Drozdovitch V., Masiuk S., Chepurny M., Zurnadzhy L. Y., Hatch M., Berrington de Gonzalez A., Thomas G. A., Tronko M. D., Getz G., Chanock S. J., Radiation-related genomic profile of papillary thyroid carcinoma after the Chernobyl accident. Science 372, eabg2538 (2021). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Behjati S., Gundem G., Wedge D. C., Roberts N. D., Tarpey P. S., Cooke S. L., Van Loo P., Alexandrov L. B., Ramakrishna M., Davies H., Nik-Zainal S., Hardy C., Latimer C., Raine K. M., Stebbings L., Menzies A., Jones D., Shepherd R., Butler A. P., Teague J. W., Jorgensen M., Khatri B., Pillay N., Shlien A., Futreal P. A., Badie C., ICGC Prostate Group, McDermott U., Bova G. S., Richardson A. L., Flanagan A. M., Stratton M. R., Campbell P. J., Mutational signatures of ionizing radiation in second malignancies. Nat. Commun. 7, 12605 (2016). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

