Tamarixetin Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Progression by Targeting DPP7-Mediated WNT3A/β-Catenin Signalling Pathway
- PMID: 40845164
- PMCID: PMC12372979
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.70787
Tamarixetin Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Progression by Targeting DPP7-Mediated WNT3A/β-Catenin Signalling Pathway
Abstract
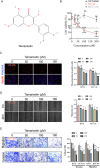
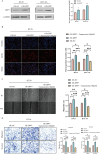
Colorectal cancer (CRC) patients have had limited benefits from conventional chemotherapy, highlighting the need for improved therapeutic strategies. Natural compounds have emerged as promising alternatives due to their potent anti-cancer properties and reduced side effects. Tamarixetin is an O-methylated flavonol derived from Azadirachta indica, but its potential and clinical utility to suppress CRC progression remain unknown. To figure out the underlying mechanism, the inhibitory effects of Tamarixetin on CRC were evaluated by in vitro assays; the validation of Tamarixetin-mediated tumour suppression was performed with CRC xenografts and patient-derived organoids. Our results demonstrated that Tamarixetin significantly reduced the proliferation of CRC cells (HT-29 and HCT-116) in a dose-dependent manner, with minimal effects on normal colonic epithelial cells (NCM460). Furthermore, Tamarixetin inhibited proliferation, migration, and invasion of CRC cells, leading to reduced xenograft tumour growth and sensitising CRC to Oxaliplatin. Mechanistically, The expression and protein levels of DPP7 in CRC cells were suppressed by Tamarixetin, which lead to the downregulation of WNT3A/β-catenin signalling pathway. This study highlights Tamarixetin as a promising natural compound for CRC treatment by interfering with DPP7-mediated WNT3A/β-catenin signalling pathway. These findings provide a novel therapeutic strategy to improve outcomes of CRC.
Keywords: DPP7; Tamarixetin; WNT3A/β‐catenin Signalling pathway; anticancer therapy; colorectal cancer.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mechanism of ABCD3 inhibiting colorectal cancer progression by regulating Wnt/β-catenin.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jul 16;52(1):727. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10825-4. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40668324
-
A novel drug prejudice scaffold-imidazopyridine-conjugate can promote cell death in a colorectal cancer model by binding to β-catenin and suppressing the Wnt signaling pathway.J Adv Res. 2025 Jun;72:615-632. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.07.022. Epub 2024 Jul 25. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 39067696 Free PMC article.
-
TsR-0072 inhibits colorectal cancer progression through modulating lipid and vitamin D3 metabolic reprogramming and inactivating the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2531253. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2531253. Epub 2025 Jul 13. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 40652418 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Mesenchymal Markers in Colorectal Cancer Metastasis.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jul 4;52(1):673. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10745-3. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40613936 Review.
-
The use of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 May;12(15):iii-ix, xi-162. doi: 10.3310/hta12150. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18462574
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GZC20240333/Postdoctoral Fellowship Program of CPSF under Grant Number
- Science and Technology Projects in Guangzhou
- 2024A04J3707/Guangzhou Science and Technology Plan Basic and Applied Basic Research Funding Project
- A2023398/Guangdong Medical Science and Technology Research Fund Project
- 21623305/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

