Ultrasonication-driven optimization of cricket protein nanoemulsions: influence of pH and rheological stabilizers
- PMID: 40845770
- PMCID: PMC12398834
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2025.107522
Ultrasonication-driven optimization of cricket protein nanoemulsions: influence of pH and rheological stabilizers
Abstract
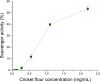
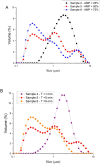
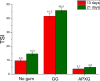
This study investigates the formulation of sustainable nanoemulsions using cricket protein as a natural emulsifier and linseed oil as the dispersed phase, emphasizing the effects of pH, ultrasonication, and rheological modifiers on emulsion stability and structure. Surface and interfacial tension analyses revealed significant reductions with increasing protein concentration, stabilizing at ≥1 g/L. At alkaline pH (≥12), interfacial tension became unmeasurable due to complete phase merging, attributed to enhanced protein solubility and surface activity. Droplet size distribution exhibited bimodal patterns across all pH levels, with the smallest Sauter diameter (0.54 μm) and optimal span (1.91) achieved at pH 12.5. Ultrasonication parameters (amplitude and sonication time) were optimized using response surface methodology. The smallest droplet size (0.365 μm) was predicted at 63 % amplitude and 9.6 min of sonication. However, higher energy inputs also increased polydispersity, likely due to droplet recoalescence in the absence of sufficient emulsifier. To enhance stability, guar gum (GG) and advanced performance xanthan gum (APXG) were tested. APXG, particularly at ≥0.25 wt%, significantly improved viscoelasticity (G' > G″) and increased consistency (K = 9.87 Pa·sn at 0.5 wt%), forming gel-like structures and reducing the Turbiscan Stability Index (TSI) over a 21-day period. These results underscore the critical roles of pH, ultrasonic processing, and rheological modification in designing robust nanoemulsions. The integration of cricket protein and APXG under optimized conditions offers a promising platform for stable, eco-friendly emulsions in functional food and nutraceutical applications.
Keywords: Cricket protein; Food processing; Nanoemulsion; Sustainable; Ultrasonic.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Sustainable stabilization of microfluidized chia oil nanoemulsions by mixed proteins.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 26;15(1):31435. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-16920-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40858666 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative evaluation of stability and interfacial characteristics of Pickering emulsions co-stabilized by zein and hydrocolloids: Role of charge profile, emulsifying ability, and rheological properties.Food Res Int. 2025 Oct;218:116948. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2025.116948. Epub 2025 Jun 24. Food Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40790721
-
Ultrasonic engineering of bovine serum albumin nanoparticles for high internal phase Pickering emulsions: Interfacial behavior, microstructural evolution and stabilization enhancement.Ultrason Sonochem. 2025 Aug 28;121:107543. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2025.107543. Online ahead of print. Ultrason Sonochem. 2025. PMID: 40885097 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Muscio A., Sisto R. Are agri-food systems really switching to a circular economy model? Implications for European research and innovation policy. Sustainability. 2020;12:5554. doi: 10.3390/su12145554. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

